NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 SST Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Question-1
Define an Ecosystem.
Solution:
An ecosystem is a community of plants, animals and smaller organisms that live,feed, reproduce and interact in the same area or environment. Some ecosystems are very large. For example, many bird species nest in one place and feed in a completely different area. On the other hand, some ecosystems may be physically small, such as you would find in a meadow at he edge of a forest, or in a coral reef in the ocean.How does everything fit together in a forest ecosystem versus a meadow ecosystem?
While some species may be found naturally in both areas, the species that live in the forest ecosystem are usually very different from those that inhabit the meadow, even though the two environments are right next to each other. In other words, if we protect existing natural habitats, we will help to maintain biodiversity (biodiversity is the variety of life in all its forms, levels and combinations). Unfortunately, natural habitats and their ecosystems are more and more endangered because of the damaging environmental effects of growing human populations everywhere.
Question-2
What factors are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India?
Solution:
Distribution of plants and animals on the earth is determined mainly by climate. However the other factors are soil, relief and drainage, though most of them are also interrelated.
Question-3
What is a bio-reserve? Give two examples.
Solution:
A protected area reserved for the conservation of endangered species of flora (plants) and fauna (animals) in their natural habitat. The Sunderbans in the West Bengal and Nanda Devi in Uttaranchal are the two examples.
Uses of Biosphere Reserve
- In a biosphere reserve, endangered species of animals and plants are protected.
- This important heritage (of plants and animals) is transmitted to the future generations in all its natural vigour and glory.
- The surrounding areas are reserved for research work for the betterment of flora and fauna.
Question-4
Name two animals having habitat in tropical and montane type of vegetation.
Solution:
The common animals found in the tropical forests are elephants and monkeys and the common animals found in the montane forests are Kashmir stag and spotted dear.
Question-5
Distinguish Between Flora and Fauna.
Solution:
Flora
The flora of a country consists of plant kingdom of that country. It covers trees in the forests, other flowering and non-flowering frees grown by man, grassland, scrubs, fens, etc. India possesses about 47,000 different species of plants and 5,000 of them are exclusively found in India.
Fauna
The fauna of a country consists of birds, fish and animals. It also includes amphibians, reptiles, mammals, small insects and worms. The fauna of India is quite rich and varied. There are about 89,000 species in India.
Question-6
Distinguish Between Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous Forests
Solution:
Tropical Evergreen Forests:
Evergreen forests (or Tropical Rain Forests) are found on the rainy parts of the Western Ghats and the island groups of Lakshadweep and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Ebony, mahogany and rosewood are the most important trees of the Evergreen Forests.Teak is the most dominant species of the deciduous forests. Other trees found here are bamboos, sal, shisham, sandalwood and khair.
Deciduous Forests:
Deciduous forests are found mostly in the eastern parts of the country – northeastern states along the foothills of the Himalayas, Jharkhand, West Orissa and Chhattisgarh and the eastern slopes of the Western Ghats.
Trees of the Evergreen Forests don’t shed their leaves at one and the same time, so these forests remain evergreen.The trees of the deciduous Forests shed their leaves for about six to eight weeks in summer.
Question-7
Name different types of Vegetation found in India and describe the vegetation of high altitudes.
Solution:
The following major types of vegetation may be identified in our country:
- Tropical Rain Forests
- Tropical Deciduous Forests
- Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs
- Montane Forests
- Mangrove Forests
The vegetation of high altitudes are Montane Forests. In mountainous areas, the decrease in temperature with increasing altitude leads to the corresponding change in natural vegetation. As such, there is a succession of natural vegetation belts in the same order as we see from the tropical to the tundra region. The wet temperate type of forests are found between a height of 1000 and 2000 metres. Evergreen broad-leaf trees such as oaks and chestnuts predominate. Between 1500 and 3000 metres, temperate forests containing coniferous trees like pine, deodar, silver fir, spruce and cedar, are found. These forests cover mostly the southern slopes of the Himalayas and places having high altitude in southern and northeast India.
At higher elevations, temperate grasslands are common. At high altitudes, generally more than 3,600 meters above sea level, temperate forests and grasslands give way to the Alpine vegetation. Silver fir, junipers, pines and birches are the common trees of these forests. However, they get progressively stunted as they approach the snow-line. Ultimately through shrubs and scrubs, they merge into the Alpine grasslands. These are used extensively for grazing by nomadic tribes like the Gujjars and the Bakarwals. At higher altitudes, mosses and lichens form part of tundra vegetation. The common animals found in these forests are Kashmir stag, spotted dear, wild sheep, jack rabbit, Tibetan antelope, yak, snow leopard, squirrels, Shaggy horn wild ibex, bear and rare red panda, sheep and goats with thick hair.
Question-8
Quite a few species of plants and animals are endangered in India. Why?
Solution:
Quite a few animal species are endangered and some have become extinct. The main causes for this major threat to nature are hunting by greedy hunters for commercial purposes, pollution due to chemical and industrial waste, acid deposits, introduction of alien species and reckless cutting of the forests to bring land under cultivation and inhabitation, which are also responsible for the imbalance.
Question-9
Why has India a rich heritage of flora and fauna?
Solution:
Our country India is one of the twelve-mega bio-diversity countries of the world. With about 47,000 plant species India occupies tenth place in the world and fourth in Asia in plant diversity. There are about 15,000 flowering plants in India, which account for 6 percent in the world’s total number of flowering plants. The country has many non-flowering plants such as ferns, algae and fungi. India also as 89,000 species of animals as well as a rich variety of fish in its fresh and marine waters.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Question 1.
Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below:
(i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong to?
Ans:
(a) Thndra
(b) Tidal
(c) Himalayan
(d) Tropical Evergreen
Ans:
(d) Tropical Evergreen
(ii) Cinchona trees are found in the areas of rainfall more than
(a) 100 cm
(b) 50 cm
(c) 70 cm
(d) less than 50 cm
Ans:
(a) 100 cm
(iii) In which of the following states is the Simlipal’ bio-reserve located?
(a) Punjab
(b) Delhi
(c) Odisha
(d) West Bengal
Ans:
(c) Odisha
(iv) Which one of the following bio-reserves of India is not included in the world network of bioreserves?
(a) Manas
(b) Nilgiri
(c) Gulf of Mannar
(d) Nanda devi
Ans:
(a) Manas
Question 2.
Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) Define an ecosystem.
Ans:
An ecosystem refers to all the plants, animals and human beings interdependent and interrelated to
(ii) What factors are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India?
Ans:
The factors that are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India are:
Relief
(a) Land: The nature of land influences the type of vegetation. Land which is flat is devoted to agriculture, undulating land encourages the growth of grass and woodlands where animals live.
(b) Soil: Different types of soils support different types of vegetation. Cactus and thorny bushes grow well in the desert, marshy deltaic soils and conical trees in the hill slopes.
Climate
(a) Temperature affects the types of vegetation and its growth. Trees growth differ depending on where they are located in the mountains.
(b) The variation in the duration of sunlight affects the growth of trees. In summer trees grow faster as the sun shines for a longer time.
(c) Precipitation: Areas of heavy rainfall have denser vegetation than areas of less rain. There is a dense growth of trees in regions where the South West Summer Monsoons cause heavy rain e.g., windward slopes of the Western Ghats.
(iii) What is a bio reserve? Give two examples.
Ans:
A bio reserve is an ecosystem having plants and animals of unusual scientific and natural instincts. These are preserved in their natural environment.
(iv) Name two animals having their habitat in montane and tropical types of vegetation.
Ans:
The Tibetan antelope and the Kashmir stag have their habitat in the Montane vegetation. In the Tropical Evergreen Forests bats and sloths are found and in the Tropical Deciduous Forests, snakes and tortoises exist.
Question 3.
Distinguish between:
(i) Flora and Fauna
Ans:
The word ‘flora’ is used to denote plants of a particular region or period and the species of animals are referred to as ‘fauna’.
(ii) Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous Forests.
Ans:
Tropical Evergreen Forests are found in regions
- where rainfall is very heavy, over 200 cm of rain.
- forests appear green all the year round as the trees shed their leaves at different times of the year.
- vegetation is luxuriant, multilayered and of great variety.
- commercially important trees are ebony, mahogany, rosewood, rubber and cinchona.
- trees are tall and have straight trunks.
Deciduous Forests are also known as Monsoon Forests.
- These are found where the rainfall is between 70 cm-200 cm.
- Trees shed their leaves for about 6-8 weeks in the dry summer.
- These forests are divided between Dry and Wet Deciduous Forests.
- Wet Deciduous Forests are found in the northeast states, foothills of the Himalayas, Jharkhand, West Odisha,
- Chhattisgarh and the eastern slopes of the Western Ghats. Important trees are bamboo, sal, shisham, Khair, Arjun, etc.
- Dry Deciduous Forests are found in the plains of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and the rainier parts of the Deccan plateau.
- Important trees are teak, sal, peepal, and neem. Trees have been cleared in some parts for cultivation and for grazing.
Question 4.
Name different types of vegetation found in India and describe the vegetation of high altitudes.
Answer:
The different types of vegetation found in India are
- Tropical Evergreen Forests
- Tropical Deciduous Forests
- Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrubs
- Montane Forests
- Mangrove Forests
Vegetation of high regions: The vegetation changes according to the changes in temperature and rainfall in the mountainous regions.
- At heights of 1000 – 2000 metres wet temperate types of forests is found. Trees such as oaks and chestnuts predominate.
- Between 1500 and 3000 metres, temperate forests with coniferous trees like pine, deodar, silver fir, spruce and cedar are found. (Northeast India etc)
- At high altitudes, Alpine vegetation is found. Important trees are silver fir, pines, and birches.
- Shrubs and scrubs are merged into the Alpine grasslands and are used for grazing.
Question 5.
Quite a few species of plants and animals are endangered in India. Why?
Answer:
Many plants and animals are endangered in India due to a number of reasons:
- Hunting of animals for commercial purposes.
- Pollution due to chemical and industrial waste, acid deposits.
- Introduction of alien species.
- Reckless cutting of the forests to bring land under cultivation and inhabitation.
As a result of these activities about 1300 plant species are endangered and 20 plants species have become extinct. Quite a few animal species are also endangered.
Question 6.
Why has India a rich heritage of flora and fauna?
Answer:
India has a rich heritage of flora and fauna due to a large variety in relief features, soil, temperature, rainfall and the length of the day which determines the hours of sunlight. Moreover, India is a very vast country
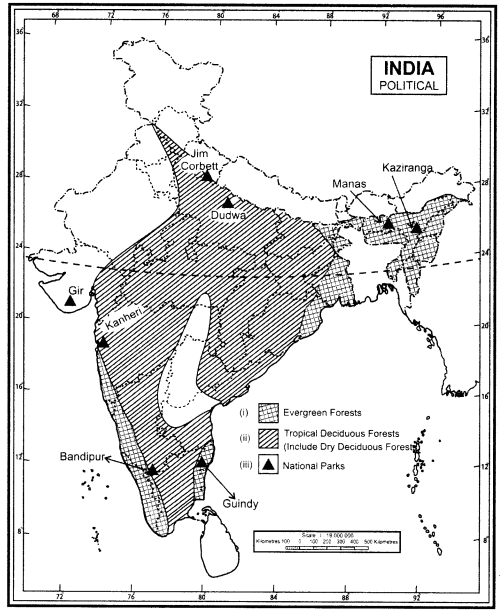
Map Skills
Question 7.
On an outline map of India, label the following.
(i) Areas of Evergreen Forests
(ii) Areas of Dry Deciduous Forests
(iii) Two national parks each in Northern, Southern, Eastern and Western parts of the Country
Answer: