NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 In Text Book Questions
Question 1.
You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper, how will you identify the contents of each test tube ?
Answer:
Take a small volume of all the three liquids in three test tubes. Dip red litmus paper strips separately in all the three. The tube in which red litmus strip turns blue, contains basic solution. Now remove the blue litmus paper and dip it one of the remaining test tubes. If the colour of the blue litmus paper changes to red, the tube contains acidic solution. In case, it remains blue then the tube contains distilled water.
More Resources
Question 2.
Why should not curd and sour substances be kept in containers made up of brass or copper ?
Answer:
Both curd and sour substances contain some acids in them. They react with copper or brass vessels to form certain salts which are of poisonous nature. Therefore, it is not advisable to keep them in these containers.
Question 3.
Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal ? Illustrate with an example. How will you test the presence of this gas ?
Answer:
Metals are mostly reactive in nature. They react with dilute acids (HCl and H2SO4) to evolve hydrogen gas. For example,
![]()
The gas burns with a pop sound when a burning candle is brought near it.
Question 4.
A metallic compound ‘A’ reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction if one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
Answer:
Since the gas is evolved with effervescence and extinguishes fire, it is expected to be CO2 gas. As calcium chloride is formed as one of the products, this means that the substance A’ can be calcium carbonate. It reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid as :
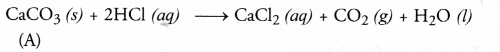
Question 5.
Aqueous solutions of HCl, HNO3 and H2SO4 etc. show acidic character while those of the compounds like ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) and glucose (C6H12O6) fail to do so. Explain.
Answer:
All the acids that are listed, have replaceable hydrogen atoms which they release in aqueous solution as H+ ions. Therefore, they show acidic character. However, both ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) and glucose (C6H12O6) do not have replaceable hydrogen atoms. They fail to evolve hydrogen gas and do not show any acidic character.
Question 6.
Why does aqueous solution of an acid (HA) conduct electricity ?
Answer:
Aqueous solution of an acid (HA) releases H+ ions or H3O+ ions and anions (A–) in solution. Since ions are the carrier of charge, the aqueous solution of an acid conducts electricity.
Question 7.
Why does not dry HCl gas change the colour of the dry litmus paper ? (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Dry HCl gas fails to release any H+ ions which means that it is not acidic. It fails to change the colour of the dry litmus paper which has also no moisture present.
Question 8.
While diluting an acid, why is it not recommended that acid should be added to water and not water to the acid ? (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Acids particularly the mineral acids like H2SO4, HNO3 and HCl etc., have strong affinity for water. The dilution process is highly exothermic in nature. The heat evolved may crack or break the container and may also convert the acid into fog which is likely to pollute the atmosphere. In order to control the heat evolved, it is advisable to add acid drop by drop to water. In case water is added to acid, then the entire acid will get itself involved in the exothermic process. It may not be possible to control the heat evolved.
Question 9.
How is concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) affected when solution of an acid is diluted with water ?
Answer:
An acid dissociates into hydronium ions (H3O+) and anions when dissolved in water. Upon dilution, the volume of the solution increases and the number of ions per unit volume decreases. Therefore, the concentration of H3O+ ions per unit volume decreases.
Question 10.
How is concentration of hydroxyl (OH–) ions affected when excess of base is dissolved in solution of sodium hydroxide ?
Answer:
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a strong base. It immediately dissociates in solution to give OH– ions and cations. Upon dissolving more of base in the solution, the concentration of OH– ions further increases.
Question 11.
You have two solutions A and B. The pH of solution A is 6 and that of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration ? Which of these is acidic and which one is basic ?
Answer:
The pH of a solution is inversely proportional to the concentration of H+ ions in solution. Lesser the pH of the solution, more will be the H+ ion concentration. The solution A with pH 6 has more H+ ion concentration than the solution with pH equal to 8. The solution A is acidic because its pH is less than 7 and the solution B is basic because its pH is more than 7.
Question 12.
What effect does concentration of H+(aq) ions have on acidic nature of absolution ?
Answer:
The acidic nature of a solution is directly related to the concentration of H+ ions. As the concentration of H+ ions increases, the acidic nature of solution also increases.
Question 13.
Do basic solutions also have H+(aq) ions ? If yes, then why are these basic ?
Answer:
Yes, basic solutions have also H+(aq) ions present in them. Actually, these solutions are prepared in water. Being a weak electrolyte, it dissociates to give H+ and OH– ions. However, the number of H+ ions is very small as compared to the number of OH– ions which are released by the base and also by water. Therefore, the solutions as a whole are of basic nature.
Question 14.
Under what soil conditions, do you think a farmer would spread or treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate) ?
Answer:
A soil usually becomes acidic when there is either a high peat content, iron minerals or there is some rotting vegetable. In order to reduce the acidic strength, ‘liming of soil’ is usually done. For this, any of the substances that have been mentioned are added to the soil since these are of basic nature.
Question 15.
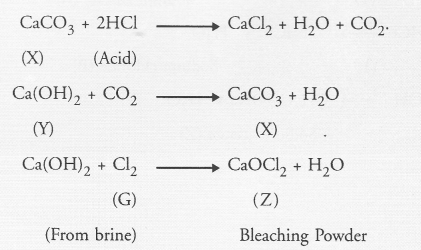
Name the substance which upon treating with chlorine gives bleaching powder. Write the chemical equation for the reaction. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Slaked lime is the substance which reacts with chlorine to give bleaching powder
![]()
Question 16.
Name the sodium compound used for softening hard water.
Answer:
Washing soda or sodium carbonate. It is chemically sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2CO3.10H2O). What will happen if the solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate is heated ?
Question 17.
Write the chemical equation involved.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide gas will evolve and sodium carbonate will be left.
![]()
Question 18.
Write the chemical equation for the reaction between Plaster of Paris and water.
Answer:
![]()
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 NCERT End Exercise
Question 1.
A solution turns red litmus blue. Its pH is likely to be
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 7
(d) 10.
Answer:
The solution is basic. Its pH is likely to be 10.
Therefore, (d) is the correct answer.
Question 2.
A solution reacts with crushed egg-shells to give a gas that turns lime water milky. The solution contains
(a) NaCl
(b) HCl
(c) LiCl
(d) KCl.
Answer:
The crushed egg-shells consist of layer of calcium carbonate which reacts with dilute HCl to evolve CO2(g). The gas turns lime water milky.
Therefore (b) is the correct choice.
Question 3.
10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralised by 8 mL of a given solution of HCl. If we take 20 mL of the same solution of NaOH, the volume of HCl solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralise will be
(a) 4 mL
(b) 8 mL
(c) 12 mL
(d) 16 mL.
Answer:
10 mL of NaOH will require HCl = 8 mL and 20 mL of NaOH will require HCl=16 mL.
Therefore, (d) is the correct answer.
Question 4.
Which of the following types of medicines is used for treating indigestion ?
(a) Antibiotic
(b) Analgesic
(c) Antacid
(d) Antiseptic.
Answer:
Antacid is used for treating indigestion.
The correct answer is (c).
Question 5.
Write the word equations and the balanced equations for the reactions when :
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron fillings.
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron fillings.
Answer:

Question 6.
Compounds like alcohol and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not characterised as acids. Describe an activity to prove it.
The chemical formula of ethyl alcohol is C2H5OH which is an alcohol and of glucose is C6H12O6. Both are organic compounds and contain hydrogen atoms. However, they do not behave as acids. (CBSE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
This can be shown by the following activity :
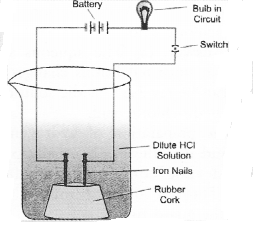
In a glass beaker, take a dilute solution of glucose (C6H12O6). Fix two small nails of iron in a rubber cork and place the cork in the beaker as shown in the figure. Connect the nails to the terminals of a 6 volt battery through a bulb. Switch on the current. The bulb will not glow. This shows that the electric current has not passed through the glucose solution. As the current is carried by the movement of ions, this shows that in solution, glucose has not given any H+ ions.
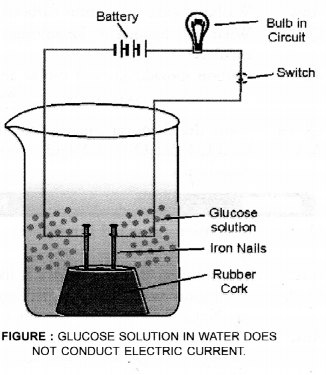
Now repeat the same experiment with ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH). The bulb will not glow in this case also. This shows that both of them do not behave as acids although they contain hydrogen atoms in their molecules.
Question 7.
Why does not distilled water conduct electricity whereas rain water does ?
Answer:
Pure water (or distilled water) is a very weak electrolyte and does not dissociate into ions. Therefore, it does not conduct electricity. However, rain water contains some dissolved acids like carbonic acid (H2CO3) and sulphurous acid (H2SO3). Actually air contains traces of both CO2 and SO2 gases which dissolve in rain water to produce corresponding acids. As a result, water becomes acidulated and gets ionised easily. Therefore, rain water conducts electricity.
Question 8.
Why does not an acid show any acidic behaviour in the absence of water ?
Answer:
An acid gets ionized only in aqueous solution i.e. in the presence of water. In other words, an acid releases H+ ions or shows acidic behaviour only in the presence of water.
Question 9.
Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator show pH as 4, 2, 12, 7 and 9 respectively. Which solution is :
(a) neutral
(b) strongly alkaline
(c) strongly acidic
(d) weakly alkaline
(e) weakly acidic
(f) Arrange the pH in increasing order of H+ ion concentration.
Answer:
(a) Neutral : D with pH = 7
(b) Strongly alkaline : C with pH = 12
(c) Strongly acidic : B with pH =2
(d) Weakly alkaline : E with pH = 9
(e) Weakly acidic : A with pH = 4
(f) Increasing order of H+ ions concentration :C<E<D<A<B
Question 10.
Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to test tube A while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is added to test tube B. In which case, fizzing occurs more vigorously and why ?
Answer:
Fizzing in the reaction is due to the evolution of hydrogen gas by the action of metal on the acid
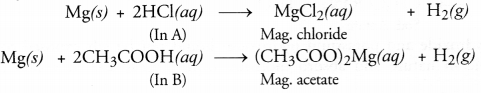
Since hydrochloric acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid, fizzing occurs more readily in tube A than in tube B. Actually hydrogen gas will evolve at more brisk speed in test tube A.
Question 11.
Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd ? Explain your answer. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
When milk changes into curd, the pH decreases. Actually, lactose (carbohydrate) present in milk gets converted into lactic acid. As more of acid is formed, pH of the medium decreases.
Question 12.
A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline ?
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd ? (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
(a) We know that fesh milk is slightly acidic due to presence of lactic acid and its pH is 6. Upon
standing, its pH slowly decreases and it becomes sour since more of acid to released. The purpose of adding baking soda or sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) is to make medium slighly alkaline. The base released will neutralise the effect of lactic acid present in milk. This will check the milk from getting sour.
(b) When milk sets as curd, it becomes more acidic and pH decreases. In the alkaline medium, it takes longer time to achieve acidic medium back so that milk may set as curd.
Question 13.
Why should Plaster of Paris be stored in a moisture-proof container ?
Answer:
In the presence of moisture, Plaster of Paris gets hydrated and changes to Gypsum which is a hard mass.
![]()
It can be no longer be used for making moulds and statues. Therefore, Plaster of Paris is kept in moisture proof containers or bags.
Question 14.
What is neutralisation reaction ? Give two examples.
Answer:
Neutralisation reaction is the reaction between acid and base dissolved in aqueous solution to form salt and water.
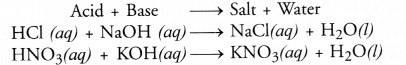
Question 15.
Both NaCl and KNO3 are neutral in nature. They neither change blue litmus red nor red litmus blue. That is why the reaction is called neutralisation reaction.
Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Uses of washing soda:
- In the manufacture of glass, soap, paper and chemicals like caustic soda (NaOH) and borax (Na2B4O7) etc.
- As a cleansing agent for domestic purposes.
Uses of baking soda:
- In baking powder used for preparing cakes.
- In antacids to reduce acidity in the stomach.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts
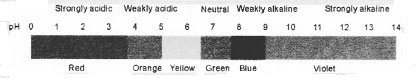
Indicators: Indicators are substances which indicate the acidic or basic nature of the solution by the colour change.
Types of Indicator: There are many types of indicators. Some common types of indicators are:
1. Natural Indicators: Indicators obtained from natural sources are called Natural Indicators. Litmus, turmeric, red cabbage, China rose, etc., are some common natural indicators used widely to show the acidic or basic character of substances.
Litmus: Litmus is obtained from lichens. The solution of litmus is purple in colour. Litmus paper comes in two colours- blue and red.
An acid turns blue litmus paper red.
A base turns red litmus paper blue.
Turmeric: Turmeric is another natural indicator. Turmeric is yellow in colour. Turmeric solution or paper turns reddish brown with base. Turmeric does not change colour with acid.
Red Cabbage: The juice of red cabbage is originally purple in colour. Juice of red cabbage turns reddish with acid and turns greenish with base.
2. Olfactory Indicator: Substances which change their smell when mixed with acid or base are known as Olfactory Indicators. For example; Onion, vanilla etc.
Onion: Paste or juice of onion loses its smell when added with base. It does not change its smell with acid.
Vanilla: The smell of vanilla vanishes with base, but its smell does not vanish with an acid.
Olfactory Indicators are used to ensure the participation of visually impaired students in the laboratory.
3. Synthetic Indicator: Indicators that are synthesized in the laboratory are known as Synthetic Indicators. For example; Phenolphthalein, methyl orange, etc.
Phenolphthalein is a colourless liquid. It remains colourless with acid but turns into pink with a base.
Methyl orange is originally orange in colour. It turns into the red with acid and turns into yellow with base.
| Indicator | Original Colour | Acid | Base |
| Red litmus | Red | No Change | Blue |
| Blue litmus | Blue | Red | No change |
| Turmeric | Yellow | No Change | Reddish brown |
| Red cabbage juice | Purple | Reddish | Greenish yellow |
| Phenolphthalein | Colourless | Colourless | Pink |
| Methyl Orange | Orange | Red | Yellow |
| Onion | n/a | No change | Smell vanishes |
| Vanilla | n/a | No change | Smell vanishes |
Acids: Acids are sour in taste, turn blue litmus red, and dissolve in water to release H+ ions.
Example: Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), Acetic Acid (CH3COOH), Nitric Acid (HNO3) etc.
Properties of Acids:
- Acids have a sour taste.
- Turns blue litmus red.
- Acid solution conducts electricity.
- Release H+ ions in aqueous solution.
Types of Acids: Acids are divided into two types on the basis of their occurrence i.e., Natural acids and Mineral acids.
(i) Natural Acids: Acids which are obtained from natural sources are called Natural Acids or Organic Acids.
Examples:
Methanoic acid (HCOOH)
Acetic acid (CH3COOH)
Oxalic acid (C2H2O4) etc.
| Organic Acids and their Sources | |
| Acids | Sources |
| Acetic acid | Vinegar |
| Ascorbic acid | Guava, amla |
| Citric acid | Lemon, orange and other citrus fruits |
| Lactic acid | Sour milk, curd |
| Methanoic acid | Ant sting, nettle sting |
| Oxalic acid | Tomato |
| Tartaric acid | Tamarind |
(ii) Mineral Acids: Acids that are prepared from minerals are known as Mineral Acids Example; Inorganic acids, man-made acids or synthetic acid are also known as Mineral Acids.
Example:
Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Sulphuric acid (H2SO4)
Nitric acid (HNO3)
Carbonic acid (H2CO3)
Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) etc.
Chemical Properties of Acid:
(i) Reaction of acids with metal: Acids give hydrogen gas along with respective salt when they react with a metal.
Metal + Acid → Salt + Hydrogen
Examples:
Hydrogen gas and zinc chloride are formed when hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc metal.

Hydrogen gas and sodium sulphate are formed when sulphuric acid reacts with sodium metal.

Test For Hydrogen Gas: The gas evolved after reaction of acid with metal can be tested by bringing a lighted candle near it. If the gas bums with a pop sound, then it confirms the evolution of hydrogen gas. Burning with pop sound is the characteristic test for hydrogen gas.
(ii) Reaction of acids with metal carbonate: Acids give carbon dioxide gas and respective salts along with water when they react with metal carbonates.
Metal carbonate + Acid → Salt + Carbon dioxide + Water
Examples:
Hydrochloric acid gives carbon dioxide gas, sodium chloride along with water when reacts with sodium carbonate.

Sulphuric acid gives calcium sulphate, carbon dioxide gas, calcium sulphate and water when it reacts with calcium carbonate

Nitric acid gives sodium nitrate, water and carbon dioxide gas when it reacts with sodium carbonate.

(iii) Reaction of acid with hydrogen carbonates (bicarbonates): Acids give carbon dioxide gas, respective salt and water when they react with metal hydrogen carbonate.
Acid + Metal hydrogen carbonate → Salt + Carbon dioxide + Water
Example:
Sulphuric acid gives sodium sulphate, Carbon dioxide gas and water when it reacts with sodium bicarbonate.

Test For Evolution of Carbon Dioxide Gas: Carbon dioxide turns lime water milky when passed through it. This is the characteristic test for carbon dioxide gas.
The gas evolved because of reaction of the acid with metal carbonate or metal hydrogen carbonate turns lime water milky. This shows that the gas is carbon dioxide gas. This happens because of the formation of a white precipitate of calcium carbonate.

But when excess of carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, it makes milky colour of lime water disappear. This happens because of formation of calcium hydrogen carbonate. As calcium hydrogen carbonate is soluble in water, thus, the milky colour of solution mixture disappears.
Common in Acids: Acids give hydrogen gas when they react with metal. This shows that all acids contains hydrogen. For example; Hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulphuric acid (H2SO4), nitric acid (HNO3), etc.
When an acid is dissolved in water, it dissociates hydrogen. The dissociation of hydrogen ion in aqueous solution is the common property in all acids. Because of the dissociation of hydrogen ion in aqueous solution, an acid shows acidic behaviour.
Examples:
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) gives hydrogen ion (H+) and chloride ion (Cl–) when it is dissolved in water.

Acetic acid (CH3COOH) gives acetate ion (CH3COO–) and hydrogen ion (H+).

Acids
Strong Acids
An acid which is completely ionised in water and produces (H+) is called Strong Acid.
Examples: Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), Nitric acid (HNO3)
Weak Acids
An acid which is partially ionised in water and thus produces a small amount of hydrogen ions (H+) is called a Weak Acid.
Example: Acetic acid (CH3COOH), Carbonic acid (H2CO3)
When a concentrated solution of acid is diluted by mixing water, then the concentration of Hydrogen ions (H+) or hydronium ion (H3O–) per unit volume decreases.
Bases: Bases are bitter in taste, have soapy touch, turn red litmus blue and give hydroxide ions (OH–) in aqueous solution.
Examples: Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) – NaOH
Calcium hydroxide – Ca(OH)2
Potassium hydroxide (caustic potash) – (KOH)
Properties of Bases:
- Have a bitter taste.
- Soapy to touch.
- Turns red litmus blue.
- Conducts electricity in solution.
- Release OH– ions in Aqueous Solution
Types of bases: Bases can be divided in two types – Water soluble and Water-insoluble.
The hydroxide of alkali and alkaline earth metals are soluble in water. These are also known as alkali.
For example; sodium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, etc. Alkali is considered a strong base.
Chemical properties of bases:
(i) Reaction of Base with Metals: When alkali (base) reacts with metal, it produces salt and hydrogen gas.
Alkali + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen
Examples: Sodium hydroxide gives hydrogen gas and sodium zincate when reacts with zinc metal.

Sodium aluminate and hydrogen gas are formed when sodium hydroxide reacts with aluminium metal.

(ii) Reaction of Base with Oxides of Non-metals: Non-metal oxides are acidic in nature. For example; carbon dioxide is a non-metal oxide. When carbon dioxide is dissolved in water it produces carbonic acid.
Therefore, when a base reacts with non-metal oxide, both neutralize each other resulting respective salt and water.
Base + Non-metal oxide → Salt + Water
(Non-metal oxides are acidic in nature)
Examples:
Sodium hydroxide gives sodium carbonate and water when it reacts with carbon dioxide.

Calcium hydroxide gives calcium carbonate and water when it reacts with carbon dioxide.

(iii) Neutralisation Reaction: An acid neutralizes a base when they react with each other and respective salt and water are formed.
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
Since, the reaction between acid and base both neutralize each other, hence, it is also known as Neutralization Reaction.
Examples: Sodium chloride and water are formed when hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide (a strong base).

In a similar way, calcium chloride is formed along with water when hydrochloric acid reacts with calcium hydroxide (a base).

(iv) Reaction of Acid with Metal Oxides: Metal oxides are basic in nature. Thus, when an acid reacts with a metal oxide both neutralize each other. In this reaction, the respective salt and water are formed.
Acid + Metal Oxide → Salt + Water
(Metal oxides are basic in nature)
Examples:
Calcium is a metal, thus, calcium oxide is a metallic oxide which is basic in nature. When an acid, such as hydrochloric acid, reacts with calcium oxide, neutralization reaction takes place and calcium chloride, along with water is formed.

Similarly, when sulphuric acid reacts with zinc oxide, zinc sulphate and water are formed.

Common in all bases: A base dissociates hydroxide ion in water, which is responsible for the basic behaviour of a compound.
Example: When sodium hydroxide is dissolved in water, it dissociates hydroxide ion and sodium ion.

Similarly, when potassium hydroxide is dissolved in water, it dissociates hydroxide ion and potassium ion.

Thus, the base shows its basic character because of dissociation of hydroxide ion.
Neutralisation Reaction: When an acid reacts with a base, the hydrogen ion of acid combines with the hydroxide ion of base and forms water. As these ions combine together and form water instead of remaining free, thus, both neutralize each other.

Example: When sodium hydroxide (a base) reacts with hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide breaks into a sodium ion and hydroxide ion and hydrochloric acid breaks into hydrogen ion and chloride ion.
Hydrogen ion and hydroxide ion combine together and form water, while sodium ion and chloride ion combine together and form sodium chloride.

Dilution of Acid and Base: The concentration of hydrogen ion in an acid and hydroxide ion in a base, per unit volume, shows the concentration of acid or base.
By mixing of acid to water, the concentration of hydrogen ion per unit volume decreases. Similarly, by addition of base to water, the concentration of hydroxide ion per unit volume decreases. This process of addition of acid or base to water is called Dilution and the acid or base is called Diluted.
The dilution of acid or base is exothermic. Thus, acid or base is always added to water and water is never added to acid or base. If water is added to a concentrated acid or base, a lot of heat is generated, which may cause splashing out of acid or base and may cause severe damage as concentrated acid and base are highly corrosive.
Strength of Acid and Base: Acids in which complete dissociation of hydrogen ion takes place are called Strong Acids. Similarly, bases in which complete dissociation of hydroxide ion takes place are called Strong Bases.
In mineral acid, such as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, nitric acid, etc. hydrogen ion dissociates completely and hence, they are considered as strong acids. Since inorganic acids hydrogen ions do not dissociate completely, so they are weak acids.

For water or neutral solutions : pH = 7
For acidic solutions : pH < 7
For basic solution : pH > 7
Universal Indicator: Using a litmus paper, phenolphthalein, methyl orange, etc. only the acidic or basic character of a solution can be determined, but the use of these indicators does not give the idea about the strength of acid or base. So, to get the strength as well as acidic and basic nature of a given solution universal indicator is used.
Universal indicator shows different colour over the range of pH value from 1 to 14 for a given solution. Universal indicator is available both in the form of strips and solution. Universal indicator is the combination of many indicators, such as water, propanol, phenolphthalein, sodium salt, sodium hydroxide, methyl red, bromothymol blue monosodium salt, and thymol blue monosodium salt. The colour matching chart is supplied with a universal indicator which shows the different colours for different values of pH.

pH value shown by different colours role of pH everyday life:
(i) pH in our digestive system: Dilute HCl (Hydrochloric acid) helps in digestion of food (proteins) in our stomach. Excess acid in stomach causes acidity (indigestion). Antacids like magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)2] also known as milk of magnesia and sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda) are used to neutralize excess acid.
(ii) Tooth decay caused by acids: The bacteria present in our mouth converts the sugar into acids. When the pH of acid formed in the mouth falls below 5.5, tooth-decaying starts. The excess acid has to be removed by cleaning the teeth with a good quality toothpaste because these kinds of toothpaste are alkaline in nature.
(iii) Soil of pH and plant growth: Most of the plants have a healthy growth when the soil has a specific pH (close to 7) range which should be neither alkaline nor highly acidic. Therefore,
- Compound ‘X’ is Sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- Compound ‘A’ is Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4).
- Compound ‘B’ is Sodium chloride (NaCl).
- Compound ‘C’ is Sodium acetate (CH3COONa)
Salts: Salts are the ionic compounds which are produced after the neutralization reaction between acid and base. Salts are electrically neutral. There are number of salts but sodium chloride is the most common among them. Sodium chloride is also known as table salt or common salt. Sodium chloride is used to enhance the taste of food.
Characteristics of salt:
- Most of the salts are crystalline soild.
- Salts may be transparent or opaque.
- Most of the salts are soluble in water.
- Solution of the salts conducts electricity in their molten state also.
- The salt may be salty, sour, sweet, bitter and umami (savoury).
- Neutral salts are odourless.
- Salts can be colourless or coloured.
Family of Salt: Salts having common acidic or basic radicals are said to belong to the same family.
Example:
(i) Sodium chloride (NaCl) and Calcium chloride (CaCl2) belongs to chloride family.
(ii) Calcium chloride (CaCl2) and Calcium sulphate (CaSO4) belongs to calcium family.
(iii) Zinc chloride (ZnCl2) and Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) belongs to the zinc family.
Neutral, Acidic and Basic Salts:
(i) Neutral Salt: Salts produced because of reaction between a strong acid and strong base are neutral in nature. The pH value of such salts is equal to 7, i.e. neutral.
Example : Sodium chloride, Sodium sulphate. Postassium chloride, etc.
Sodium chloride (NaCl): It is formed after the reaction between hydrochloric acid (a strong acid) and sodium hydroxide (a strong base).

Sodium Sulphate (Na2SO4): It is formed after the reaction between sodium hydroxide (a strong base) and sulphuric acid ( a strong acid).

Potassium Chloride (KCl): It is formed after the reaction between potassium hydroxide (a strong base) and hydrochloric acid (a strong acid).

(ii) Acidic Salts: Salts which are formed after the reaction between a strong acid and weak base are called Acidic salts. The pH value of acidic salt is lower than 7. For example Ammonium sulphate, Ammonium chloride, etc.
Ammonium chloride is formed after reaction between hydrochloric acid (a strong acid) and ammonium hydroxide (a weak base).

Ammonium sulphate is formed after reaction between ammonium hydroxide (a weak base) and sulphuric acid (a strong acid).

(iii) Basic Salts: Salts which are formed after the reaction between a weak acid and strong base are called Basic Salts. For example; Sodium carbonate, Sodium acetate, etc.
Sodium carbonate is formed after the reaction between sodium hydroxide (a strong base) and carbonic acid (a weak acid).

Sodium acetate is formed after the reaction between a strong base, sodium hydroxide (a strong base) and acetic acid, (a weak acid).

Cause of formation of acidic, basic and neutral salts:
- When a strong acid reacts with a weak base, the base is unable to fully neutralize the acid. Due to this, an acidic salt is formed.
- When a strong base reacts with a weak acid, the acid is unable to fully neutralize the base. Due to this, a basic salt is formed.
- When equally strong acid and a base react, they fully neutralize each other. Due to this, a neutral salt is formed.
pH value of salt:
- Neutral salt: The pH value of a neutral salt is almost equal to 7.
- Acidic salt: The pH value of an acidic salt is less than 7.
- Basic salt: The pH value of a basic salt is more than 7.
Some Important Chemical Compounds
1. Common Salt (Sodium Chloride): Sodium chloride (NaCl) is also known as Common or Table Salt. It is formed after the reaction between sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid. It is a neutral salt. The pH value of sodium chloride is about 7. Sodium chloride is used to enhance the taste of food. Sodium chloride is used in the manufacturing of many chemicals.
Important chemical from sodium chloride
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): Sodium hydroxide is a strong base. It is also known as caustic soda. It is obtained by the electrolytic decomposition of solution of sodium chloride (brine). In the process of electrolytic decomposition of brine (aqueous solution of sodium chloride), brine decomposes to form sodium hydroxide. In this process, chlorine is obtained at anode and hydrogen gas is obtained at cathode as by products. This whole process is known as Chlor – Alkali process.

Use of products after the electrolysis of brine:
- Hydrogen gas is used as fuel, margarine, in making of ammonia for fertilizer, etc.
- Chlorine gas is used in water treatment, manufacturing of PVC, disinfectants, CFC, pesticides. It is also used in the manufacturing of bleaching powder and hydrochloric acid.
- Sodium hydroxide is used for degreasing of metals, manufacturing of paper, soap, detergents, artificial fibres, bleach, etc.
2. Bleaching Powder (CaOCl2): Bleaching powder is also known as chloride of lime. It is a solid and yellowish white in colour. Bleaching powder can be easily identified by the strong smell of chlorine.
When calcium hydroxide (slaked lime) reacts with chlorine, it gives calcium oxychloride (bleaching powder) and water is formed.

Aqueous solution of bleaching powder is basic in nature. The term bleach means removal of colour. Bleaching powder is often used as bleaching agent. It works because of oxidation. Chlorine in the bleaching powder is responsible for bleaching effect.
Use of Bleaching Powder:
- Bleaching powder is used as disinfectant to clean water, moss remover, weed killers, etc.
- Bleaching powder is used for bleaching of cotton in textile industry, bleaching of wood pulp in paper industry.
- Bleaching powder is used as oxidizing agent in many industries, such as textiles industry, paper industry, etc.
3. Baking Soda (NaHCO3): Baking soda is another important product which can be obtained using byproducts of chlor – alkali process. The chemical name of baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) or sodium bicarbonate. Bread soda, cooking soda, bicarbonate of soda, sodium bicarb, bicarb of soda or simply bicarb, etc. are some other names of baking soda.
Preparation Method: Baking soda is obtained by the reaction of brine with carbon dioxide and ammonia. This is known as Solvay process.

In this process, calcium carbonate is used as the source of CO2 and the resultant calcium oxide is used to recover ammonia from ammonium chloride.
Properties of Sodium Bicarbonate:
- Sodium bicarbonate is white crystalline solid, but it appears as fine powder.
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate is amphoteric in nature.
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate is sparingly soluble in water.
- Thermal decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda).
- When baking soda is heated, it decomposes into sodium carbonate, carbon dioxide and water.
2NaHCO3 + heat → Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O - Sodium carbonate formed after thermal decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate decomposes into sodium oxide and carbon dioxide on further heating.
Na2CO3 → Na2O + CO2
This reaction is known as Dehydration reaction.
Use of Baking Soda:
- Baking soda is used in making of baking powder, which is used in cooking as it produces carbon dioxide which makes the batter soft and spongy.
- Baking soda is used as an antacid.
- Baking soda is used in toothpaste which makes the teeth white and plaque free.
- Baking soda is used in cleansing of ornaments made of silver.
- Since sodium hydrogen carbonate gives carbon dioxide and sodium oxide on strong heating, thus, it, is used as a fire extinguisher.
Baking Powder: Baking powder produces carbon dioxide on heating, so it is used in cooking to make the batter spongy. Although, baking soda also produces carbon dioxide on heating, but it is not used in cooking because on heating, baking soda produces sodium carbonate along with carbon dioxide. The sodium carbonate, thus, produced, makes the taste bitter.

Baking powder is the mixture of baking soda and a mild edible acid. Generally, tartaric acid is mixed with baking soda to make baking powder.

When baking powder is heated, sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) decomposes to give CO2 and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3). CO2 causes bread and cake fluffy. Tartaric acid helps to remove bitter taste due to formation of Na2CO3.
4. Washing Soda (Sodium Carbonate)
Preparation Method: Sodium carbonate is manufactured by the thermal decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate obtained by Solvay process.

The sodium carbonate obtained in this process is dry. It is called Soda ash or Anhydrous sodium carbonate. Washing soda is obtained by rehydration of anhydrous sodium carbonate.

Since there are 10 water molecules in washing soda, hence, it is known as Sodium Bicarbonate Decahydrate.
Sodium carbonate is a crystalline solid and it is soluble in water when most of the carbonates are insoluble in water.
Use of sodium carbonate:
- It is used in the cleaning of cloths, especially in rural areas.
- In the making of detergent cake and powder.
- In removing the permanent hardness of water.
- It is used in glass and paper industries.
The water of Crystallization: Many salts contain water molecule and are known as Hydrated Salts. The water molecule present in salt is known as Water of crystallization.
Examples:
Copper sulphate pentahydrate (CuSO4.5H2O): Blue colour of copper sulphate is due to presence of 5 molecules of water. When copper sulphate is heated, it loses water molecules and turns: into grey – white colour, which is known as anhydrous copper sulphate. After adding water, anhydrous copper sulphate becomes blue again.

Acids: Substances which turn blue litmus solution red are called acids. Acids are sour in taste.
Bases: Substances which change red litmus solution blue are called bases. They are bitter in taste.
Mineral Acids: Acids which are obtained from minerals like sulphates, nitrates, chlorides etc. are called mineral acids, example, H2SO4 (Sulphuric acid), HNO3 (Nitric acid) and HCl (Hydrochloric acid).
Organic Acids: Acids which are obtained from plants and animals are called organic acids. Example citric acid, ascorbic acid, tartaric acid, lactic acid, acetic acid.
Hydronium Ions: They are formed by the reaction of H+ (from acid) and H2O. It is because H+ is unstable.
Universal Indicator: A universal indicator is a mixture of indicators which shows a gradual but well-marked series of colour changes over a very wide range of change in concentration of H+ ions.
Strong Acids: Acids which dissociate into ions completely are called strong acids. Example, H2SO4, HCl.
Weak Acids: Acids which do not dissociate into ions completely are called weak acids. Example, citric acid, acetic acid.
Chemical Properties of Acids:
- Acids react with active metals to give salt and hydrogen gas.
- Acids react with metal carbonates and metal hydrogen carbonates to give salt, water and carbon dioxide.
- Acids react with bases to give salt and water. This reaction is called a neutralization reaction.
- Acids react with metal oxides to give salt and water.
Chemical Properties of Bases:
- Reaction with metals: Certain metals such as zinc, aluminium and tin react with alkali solutions on heating and hydrogen gas is evolved.
- Reaction with acids: Bases react with acids to form salt and water.
Indicators: Indicators are substances which indicate the acidic or basic nature of the solution by their colour change.
pH Scale: A scale for measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
The pH of a solution is defined as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration in moles per litre.
pH = -log [H+]
pH = -log [H3O+]
where [H+] or [H3O+] represents concentrations of hydrogen ions in a solution.
- The pH of a neutral solution is 7.
- The pH of an acidic solution is < 7.
- The pH of a basic solution is > 7.
Some Important Compounds and their Uses:
Equations of Acids, Bases and Salts:
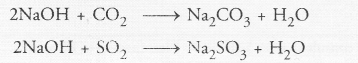
- Acid + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen gas
H2SO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + H2 - Base + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen gas
2NaOH + Zn → Na2ZnO2 (Sodium zincate) + H2 - Base + Acid → Salt + Water
NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) - Acids give hydronium ions in water
HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl– - Bases generate OH- ions in water
NaOH (aq) + H2O → Na+ (aq) + O– (aq)
Reactions Of Important Chemical Compounds:
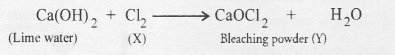
- Preparation of Bleaching powder: By the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O - On heating, baking soda liberates CO2

- Preparation of Plaster of Paris:

NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases And Salts
Short Answer Type Questions
1.Match the acids given in Column (A) with their correct source given in Column (B).

Ans.(a) —> (iv) (b) —> (iii) (c) —> (ii) (d) —> (i)
Lactic acid is present in curd, acetic acid is present in vinegar, citric acid is present in lemon and oxalic acid is present in tomato.
2.What will be the action of the following substances on litmus paper?
Dry.HCl gas, Moistened NH3 gas, Lemon juice, Carbonated soft drink, Curd, Soap solution.
Ans.Dry HC1 gas will not have any effect on litmus paper. Moistened NH3 gas will turn red litmus blue. Curd, lemon juice, carbonated soft drink will turn blue litmus red. Soap solution will turn red litmus blue.
3.Name the acid present in ant sting and give its chemical formula. Also give the common method to get relief from the discomfort caused by the ant sting.
Ans. Ant sting contains methanoic acid (formic acid). Its chemical formula is HCOOH. The common method to get relief is to apply paste of NaCO3 (baking soda) on it.
4.What happens when nitric acid is added to egg-shell?
Ans. Egg-shell is made up of calcium carbonate which will react with HNO3 to form C2(g) andH2(l) along with calcium nitrate.
CaCO3+2HNO3⟶Ca(NO3)2+CO2+H2O
5.A student prepared solutions of (i) an acid and (ii) a base in two separate
beakers. She forgot to label the solutions and litmus paper is not available in the laboratory. Since, both the solutions are colourless, how will she distinguish between the two?
Ans.Add phenolphthalein to a portion of each solution in separate test tube. If it turns pink, the beaker contains base whereas if it remains colourless, it is an acid.
If phenolphthalein is not available, pH paper can be used. Acid will turn pH paper red, base will turn pH paper blue.
6.How would you distinguish between baking powder and washing soda by heating?
Ans.

7.Salt A commonly used in bakery products on heating gets converted into another salt B which itself is used for removal of hardness of water and a gas C is evolved. The gas C when passed through lime water, turns it milky. Identify A, B and C.
Ans.

8.In one of the industrial processes used for manufacture of sodium hydroxide, a gas X is formed as by-product. The gas X reacts with lime water to give a compound Y which is used as a bleaching agent in chemical industry. Identify X and Y giving the chemical equation of the reactions involved.
Ans.

9.What are strong and weak acids? In the following list of acids, separate strong acids from weak acids.
Hydrochloric acid, citric acid, acetic acid, nitric acid, formic acid, sulphuric acid.
Ans. Strong acids are those acids which are completely ionised in aqueous solution. Weak acids are those which do not ionise completely in aqueous solution. Strong adds: HC1,HNO3 , H2SO4 Weak acids: Citric acid, acetic acid, formic acid
1O.A metal carbonate X on reacting with an acid gives a gas which when passed through a solution Y gives the carbonate back. On the other hand, a gas G that is obtained at anode during electrolysis of brine is passed on dry Y, it gives a compound Z, used for disinfecting drinking water. Identify X, Y, G and Z.
Ans.


11.A dry pellet of a common base B, when kept in open absorbs moisture and turns sticky. The compound is also a by-product of chlor-alkali process. Identify B. What type of reaction occurs when B is treated with an acidic oxide? Write a balanced chemical equation for one such solution.
Ans.‘B’ is NaOH. It absorbs moisture from atmosphere because it is hygroscopic in nature. It is obtained by product of chlor-alkali process.

‘B’ reacts with acidic oxide CO2 to form salt and water. This reaction is called neutralisation reaction.
12.A sulphate salt of Group 2 element of the Periodic Table is a white, soft substance, which can be moulded into different shapes by making its dough. When this compound is left in open for sometime, it becomes a solid mass and cannot be used for moulding purposes. Identify the sulphate salt. Why does it show such a behaviour? Give the reaction involved.
Ans. Salt is CaS04 1/2 H20, Plaster of Paris, white soft substance. It can be dough,
moulded into different shapes, as 2 moles of CaS04 share 1 mole of HgO molecule.
CaSO41/2H2O+32H2O⟶CaSO42H2O
When it is left in open, it becomes solid mass CaS042H20 (Gypsum) which cannot be used for moulding purposes as it is hard solid mass.
13.Identify the compound X on the basis of the reactions given below. Also, write the name and chemical formulae of A, B and C.

Ans.

14.Match the important chemicals given in Column (A) with the chemical formulae given in Column (B).

Ans.

15.Fill in the missing data in the following data.


Ans.

16.When Zinc metal is treated with dilute solution of strong acid, a gas is involved which is utilized in hydrogenation of oil. Name the gas involved. Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved and also write a test to detect the gas formed.
Hydrogen gas is liberated
Ans.
Zn(s)+H2SO4(dil.)⟶ZnSO4(aq)+H2(g)
Test: Bring a burning splinter near the gas. The gas will burn with ‘Pop’ sound which shows gas is H2.
17.In the following schematic diagram for the preparation of hydrogen gas as shown in the given figure, what would happen if following changes are made ?

(а)In place of zinc granules, same amount of zinc dust is taken in the test tube.
(b)Instead of dilute sulphuric acid, dilute hydrochloric acid is taken.
(c)In place of zinc, copper turnings are taken.
(d)Sodium hydroxide is taken in place of dilute sulphuric acid and the tube
is heated.
Ans.(a)The reaction will become faster because zinc dust has more surface area.
(b)Nearly same amount of hydrogen gas will be evolved.
(c)No reaction will take place as copper is less reactive than hydrogen.
(d)The reaction will take place and hydrogen gas will be evolved.

18.For making cake, baking powder is taken. If at home your mother uses baking soda instead of baking powder in cake.
(a)How will it affect the taste of the cake and why?
(b)How can baking soda be converted into baking powder?
(c)What is role of tartaric acid added to baking soda?
Ans.(a)The cake will taste bitter due to formation of sodium carbonate.
(b)Tartaric acid should be added to baking soda to convert it into baking powder.
(c)Tartaric acid neutralizes sodium carbonate formed and will not make the taste bitter.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
Question 1.
What happens when a solution of an acid is mixed with a solution of a base in a test tube ?
(i) The temperature of the solution increases
(ii) The temperature of the solution decreases
(iii) The temperature of the solution remains the same
(iv) Salt formation takes place
(a) (i) only
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(d). Salt formation takes place in the neutralisation reaction. It is always exothermic and temperature increases.
Question 2.
An aqueous solution turns red litmus solution blue. Excess addition of which of the following solutions would reverse the change ?
(a) Baking powder
(b) Lime
(c) Ammonium hydroxide solution
(d) Hydrochloric acid
Answer:
(d). The aqueous solution is of basic nature since red litmus changes to blue. The reaction can be reversed (acidic solution) by adding excess of hydrochloric acid.
Question 3.
During the preparation of hydrogen chloride gas on a humid day, the gas is usually passed through the guard tube containing anhydrous calcium chloride. The role of anhydrous calcium chloride taken in the guard tube is to
(a) absorb the evolved gas
(b) moisten the gas
(c) absorb moisture from the gas
(d) absorb Cl– ions from the evolved gas
Answer:
(c). Anhydrous CaCl2 absorbs moisture to keep the gas in dry state. Otherwise, it will dissolve in moisture to form hydrochloric acid.
Question 4.
Which of the following salts does not contain any water of crystallisation ?
(a) Blue vitriol
(b) Baking soda
(c) Washing soda
(d) Gypsum
Answer:
(b). Baking soda (NaHCO3) does not contain any water of crystallisation.
Question 5.
Sodium carbonate is a basic salt because it is a salt of
(a) strong acid and strong base
(b) weak acid and weak base
(c) strong acid and weak base
(d) weak acid and strong base
Answer:
(d). Na2CO3 is a salt of weak acid (H2CO3) and strong base (NaOH).
Question 6.
Calcium phosphate is present in tooth enamel. Its nature is
(a) basic
(b) acidic
(c) neutral
(d) amphoteric
Answer:
(a). Ca3(PO4)2 is a salt of strong base Ca(OH)2 and weak acid H3PO4.
Question 7.
A sample of soil is mixed with water and allowed to settle. The clear supernatant solution turns the pH paper yellowish-orange. Which of the following would change the colour of this pH paper to greenish-blue ?
(a) Lemon juice
(b) Vinegar
(c) Common salt
(d) An antacid
Answer:
(d). The colour of the pH paper signifies that the solution is somewhat acidic. In order to change it to greenish-blue, we need an antacid.
Question 8.
Which of the following gives the correct increasing order of acidic strength ?
(a) Water
(b) Water
(c) Acetic acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid Water Acetic acid
Answer:
(a).
Question 9.
If a few drops of a concentrated acid accidentally spill over the hand of a student, what should be done ?
(a) Wash the hand with saline solution
(b) Wash the hand immediately with plenty of water and apply a paste of sodium hydrogen carbonate
(c) After washing hand with plenty of water, apply solution of sodium hydroxide on the hand
(d) Neutralise the acid with a strong alkali
Answer:
(b). Washing the hand initially with plenty of water gives partial relief from burning sensation. The paste of sodium hydrogen carbonate completely neutralises the effect of the acid.
Question 10.
Sodium hydrogen carbonate when added to acetic acid evolves a gas. Which of the following statements are true about the gas evolved ?
(i) It turns lime water milky
(ii) It extinguishes a burning splinter
(iii) It dissolves in a solution of sodium hydroxide
(iv) It has a pungent odour
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(b). The gas evolved is carbon dioxide (CO2). The statements (i), (ii) and (iii) are true about the gas.
Question 11.
Common salt besides being used in kitchen can also be used as the raw material for making
(i) washing soda
(ii) bleaching powder
(iii) baking soda
(iv) slaked lime
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(c).
Question 12.
One of the constituents of baking powder is sodium hydrogen carbonate. The other constituent is :
(a) hydrochloric acid
(b) tartaric acid
(c) acetic acid
(d) sulphuric acid
Answer:
(b). Tartaric acid is the other consument.
Question 13.
To protect tooth decay, we are advised to brush our teeth regularly. The nature of the tooth paste commonly used is
(a) acidic
(b) neutral
(c) basic
(d) corrosive
Answer:
(c). The basic ingredient in the paste will neutralise any acid released from the sugary’ items which we eat.
Question 14.
Which of the following statements is correct about an aqueous solution of an acid and of a base ?
(i) Higher the pH, stronger the acid
(ii) Higher the pH, weaker the acid
(iii) Lower the pH, stronger the base
(iv) Lower the pH, weaker the base
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(d). Statements (ii) and (iv) are correct.
Question 15.
The pH of the gastric juices released during digestion is
(a) less than 7
(b) more than 7
(c) equal to 7
(d) equal to 0
Answer:
(a). Gastric juices generally release hydrochloric acid during digestion. Therefore the pH is less than 7.
Question 16.
Which of the following phenomena occur when a small amount of acid is added to water ?
(i) Ionisation
(ii) Neutralisation
(iii) Dilution
(iv) Salt formation
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(b). Water helps in the ionisation of acid and also in its dilution.
Question 17.
Which one of the following can be used as an acid- base indicator by a visually impared student ?
(a) Litmus
(b) Turmeric
(c) Vanilla essence
(d) Petunia leaves
Answer:
(c). Vanilla essence is an olfactory inidicator.
Question 18.
Which of the following substances will not give carbon dioxide on treatment with dilute acid ?
(a) Marble
(b) Lime stone
(c) Baking soda
(d) Lime
Answer:
(d). Since lime (CaO) does not contain carbon, it will not give any carbon dioxide gas.
Question 19.
Which of the following is acidic in nature ?
(a) Lime juice
(b) Human blood
(c) Lime water
(d) Antacid
Answer:
(a). Lime juice is of acidic nature. It contains citric acid.
Question 20.
In an attempt to demonstrate electrical conductivity through an electrolyte, the apparatus set up is given. Which among the following statement(s) is(are) correct ?
(i) Bulb will not glow because electrolyte is not acidic
(ii) Bulb will glow because HCl is a strong acid and furnishes ions for conduction.
(iii) Bulb will not glow because circuit is incomplete
(iv) Bulb will not glow because it depends upon the type of electrolytic solution
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) only
(d) (iv) only
Answer:
(c). Bulb will glow because the acid will furnish ions which conduct electricity.
Question 21.
Which of the following is used for dissolution of gold ?
(a) Hydrochloric acid
(b) Sulphuric acid
(c) Nitric acid
(d) Aqua regia.
Answer:
(d). For the details of aqua regia.
Question 22.
Which of the following is not a mineral acid ?
(a) Hydrochloric acid
(b) Citric acid
(c) Sulphuric acid
(d) Nitric acid.
Answer:
(b). Citric acid is an organic acid present in citrus fruits. It is not a mineral acid.
Question 23.
Which of the following is not a base ?
(a) NaOH
(b) KOH
(c) NH4OH
(d) C2H5OH.
Answer:
(d). Ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) is not a base. It is an alcohol and is very weakly acidic in nature.
Question 24.
Which of the following statements is not correct ?
(a) All metal carbonates react with acid to give a salt, water and carbon dioxide
(b) All metal oxides react with water to give salt and acid
(c) Some metals react with acids to give salt and hydrogen
(d) Some non metal oxides react with water to form an acid
Answer:
(b). The statement is not correct as the metal oxide reacts with water to form metal hydroxide.
Question 25.
Match the chemical substances given in Column (A) with their appropriate application given in Column (B)
| Column (A) | Column (B) |
| (1) Bleaching powder | (i) Constituent of glass |
| (2) Baking soda | (ii) Production of H2 and Cl? |
| (3) Borax | (iii) Decolourisation |
| (4) Sodium chloride | (iv) Antacid |
(a) 1—(ii), 2—(i), 3—(iv), 4—(iii)
(b) 1—(iii), 2—(ii), 3—(iv), 4—(i)
(c) 1—(iii), 2—(iv), 3—(i), 4—(ii)
(d) 1—(ii), 2—(iv), 3—(i), 4—(iii)
Answer:
(c).
Question 26.
Equal volumes of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide solutions of same concentration are mixed and the pH of the resulting solution is checked with a pH paper. What would be the colour obtained ?
(a) Red
(b) Yellow
(c) Green
(d) Blue
Answer:
(c). pH paper will acqure green colour which indicates that the solution is of neutral nature.
Question 27.
Which of the following is(are) true when HCl (g) is passed through water ?
(i) It does not ionise in the solution as it is a covalent compound.
(ii) It ionises in the solution
(iii) It gives both hydrogen and hydroxyl ions in the solution
(iv) It forms hydronium ion in the solution due to the combination of hydrogen ion with water molecule
(a) (i) only
(b) (iii) only
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(c). Both are true.
Question 28.
Which of the following statements is true for acids ?
(a) Bitter and change red litmus to blue
(b) Sour and change red litmus to blue
(c) Sour and change blue litmus to red
(d) Bitter and change blue litmus to red
Answer:
(c). Both are the characteristics of acids.
Question 29.
Which of the following are present in a dilute aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid ?
(a) H3O+ + Cl–
(b) H3O+ + OH–
(c) Cl– + OH–
(d) unionised HCl
Answer:
(a). HCl will react with water as follows :
HCl (l) + H2O(l) ———> H3O+(aq) + Cl–(aq)
Question 30.
Identify the correct representation of reaction occurring during chloralkali process
(а) 2NaCl(l) + 2H2O(l) ———–>2NaOH(s) + Cl2(g) + H2(g)
(b) 2NaCI(aq) + 2H2O (aq) ———–> 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) + H2 (aq)
(c) 2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) ———–> 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(aq) + H2(g)
(d) 2NaCl (aq) + 2H2O (l) ———–> 2NaOH (aq) + Cl2(g) + H2(g)
Answer:
(d). It is the correct answer since the physical states of all the species involved are correct.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Short Answer Questions
Question 31.
Match the acids given in column (A) with their correct sources given in column (B)
| Column (A) | Column (B) |
| (a) Lactic acid | (i) Tamarind |
| (b) Acetic acid | (ii) Lemon |
| (c) Citric acid | (iii) Vinegar |
| (d) Tartaric acid | (iv) Curd |
Answer:
(a)-(iv)
(b)-(iii)
(c)-(ii)
(d)-(i)
Question 32.
Match the important chemicals given in Column (A) with the chemical formulae given in Column (B)
| Column (A) | Column (B) |
| (a) Plaster of Paris | (i) Ca(OH)2 |
| (b) Gypsum | (ii) CaSO4.½ H2O |
| (c) Bleaching Powder | (iii) CaS04.2H7O |
| (d) Tartaric acid | (iv) CaOCl2 |
Answer:
(a)-(ii) ;
(b)-(iii) ;
(c)-(iv) ;
(d)-(i)
Question 33.
What will be the action of the following substances on blue litmus paper ?
Answer:
Dry HCl gas, Moistened NH3 gas, Lemon juice, Carbonated soft drink, Curd, Soap solution.
It will become red, will remain blue, will become red, will become red, will become red, will remain blue.
Question 34.
Name the acid present in ant sting and give its chemical formula. Also give the common method to get relief from the discomfort caused by the ant sting.
Answer:
The acid present in ant sting is methanoic acid or formic acid. Its chemical formula is HCOOH. Being poisonous in nature, it causes pain and irritation. Even blisters may appear on the stung area. One should immediately rub the stung area with a mild base like baking soda (NaHCO3). It will react with formic acid to form salt and water. Its poisonous effect will be completely neutralised.
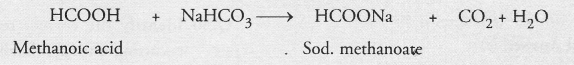
Remember : We should never apply sodium hydroxide pellets or solution directly or the affected portion. Being strongly corrosive in nature, it will aggrievate pain by forming more blisters. However, sodium hydrogen carbonate can be applied.
Question 35.
What happens when egg shell is placed in concentrated nitric acid taken in a beaker ?
Answer:
Egg shell contains calcium carbonate as its main constituent. When dipped in concentrated nitric acid, calcium carbonate reacts to evolve carbon dioxide. As a result, egg shell slowly dissolves.
![]()
Question 36.
A student prepares solutions of (i) an acid and (ii) a base in two separate beakers. She forgets to label the solutions and litmus paper is not available in the laboratory. Since both the solutions are colourless, how will she distinguish between the two ?
Answer:
Phenolphthalein and methyl orange are also acid-base indicators. They can be used in place of litmus.
Procedure : Transfer a portion of the colourless solutions to two glass tubes. Add one or two drops of henolphthalein indicator to these. An acid solution will remain colourless while the solution of base will ecome pink. Now, repeat the experiment with methyl orange indicator. In acid solution, the indicator will become reddish while in base, it will be yellowish.
Question 37.
How would you distinguish between baking soda and washing soda upon heating ?
Answer:
Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3). Upon heating, it will evolve CO2 gas which upon passing through lime water, will make it milky.
![]()
Washing soda is sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2CO3.10H2O). Upon heating, it will not evolve any gas.
![]()
Question 38.
Salt ‘A’ commonly used in bakery products on heating gets converted into another salt ‘B which itself is used for the removal of hardness of water and a gas ‘C’ is evolved. The gas ‘C’ when passed through lime water, turns it milky. Identify A, B and C.
Answer:
The salt ‘A’ is sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda) and is commonly used in bakeries as a constitutent of baking power. Upon heating, it changes to sodium carbonate ‘B’ and evolves carbon dioxide gas ‘C’.

Sodium carbonate removes hardness from water while CO2 gas turns lime water milky.
Question 39.
In one of the industrial processes used for the manufacture of sodium hydroxide, a gas ‘X’ is formed as by-product. The gas ‘X’ reacts with lime water to give a compound ‘Y’ which is used as a bleaching agent in chemical industry. Identify ‘X’ and ‘Y’ giving the chemical equation of the reactions involved.
Answer:
Sodium hydroxide is manufactured by the electrolysis of a strong solution of sodium chloride (called brine). As a result, chlorine (X) is evolved at anode while hydrogen at cathode. Chlorine reacts with lime water containing slaked lime to form bleaching power (Y)
Question 40.
Fill in the missing data in the following table
Answer:

Question 41.
What are strong and weak acids ? In the following list of acids, separate strong acids from weak acids.
Hydrochloric acid, citric acid, acetic acid, nitric acid, formic acid, sulphuric acid.
Answer:
For the definitions of strong and weak acids and bases,
An acid may be defined as a substance which releases one or more H+ ions in aqueous solution. These ions exist as hydronium (H2O+) ions.
A base may be defined as a substance capable of releasing one or more OH– ions in aqueous solution.
In general, mineral acids are strong acids while organic acids are weak. From the available list :
Strong acids : Hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, sulphuric acid.
Weak acids : Citric acid, acetic acid, formic acid.
Question 42.
When zinc metal is treated with a dilute solution of a strong acid, a gas is evolved which is utilised in the hydrogenation of oils. Name the gas evolved. Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved and also write a test to detect the gas formed.
Answer:
The gas evoloved is hydrogen. The gas burns brightly with a pop sound when a burning splinter is brought in its contact. This causes the hydrogenation of edible liquid oils to form solid fats also called Vanaspati ghee.
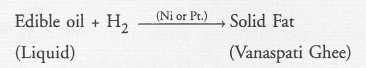
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Long Answer Questions
Question 43.
In the following schematic diagram for the preparation of hydrogen gas as shown in the figure, what would happen if following changes are made ?
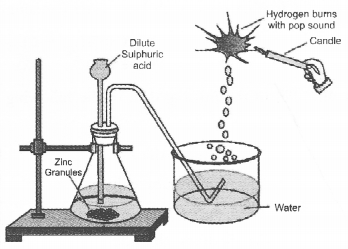
(a) In place of zinc granules, same amount of zinc dust is taken in the test tube
(b) Instead of dilute sulphuric acid, dilute hydrochloric acid is taken
(c) In place of zinc, copper turnings are taken
(d) Sodium hydroxide is taken in place of dilute sulphuric acid and the tube is heated.
Answer:
(a) Hydrogen gas would evolve at a greater speed because zinc dust provides more surface area as compared to zinc granules.
(b) Both would react in the same way. There would be no effect on the volume of the gas evolved.
(c) Copper does not react with either dilute HCl or dilute H2SO4. No gas would evolve in both the cases.
(d) Hydrogen gas would evolve in this case also.
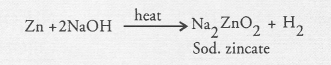
Question 44.
For making cake, baking powder is taken. If at home your mother uses baking soda instead of baking powder in cake,
(a) how will it affect the taste of the cake and why ?
(b) how can baking soda be converted into baking powder ?
(c) what is the role of tartaric acid added to baking soda ?
Answer:
Baking powder is a mixture of baking soda and tartaric acid. Out of the two, only baking soda is actually used for making bread or cake fluffy. The role of tartaric acid is to neutralise sodium carbonate formed in the reaction.
(a) If baking soda is used for making cake in place of baking powder, then cake will taste bitter since there is no tartaric acid available to neutralise sodium carbonate formed.
![]()
(b) Baking soda can be converted to baking powder by adding appropriate amount of tartaric acid.
(c) Tartaric acid as pointed above will react with sodium carbonate which makes cake bitter. This means that the cake will not taste bitter.
Question 45.
A metal carbonate (X) on reacting with an acid gives a gas which when passed through a solution (Y) gives the carbonate back. On the other hand, a gas (G) that is obtained at anode during electrolysis of brine is passed on dry substance (Y). It gives a compound (Z), used for disinfecting drinking water. Identity X, Y, G and Z.
Answer:
The gas (G) obtained at anode during the electrolysis of brine is chlorine. The compound (Z) used for disinfecting drinking water is bleaching powder. It is formed on reacting chlorine with dry slaked lime i.e., Ca(OH)2. It is denoted as ‘Y’ This means that the metal carbonate ‘X’ is calcium carbonate. Upon heating, it evolves CO2 gas which gives back ‘X’ on reacting with calcium hydroxide. The chemical reactions involved are listed :
Question 46.
A dry pellet of a common base ‘B’, when kept in open absorbs moisture and turns sticky. The compound is also formed by chloralkali process. Identify ‘B’. What type of reaction occurs when B is treated with an acidic oxide ? Write a balanced chemical equation for one such solution.
Answer:
The available information suggests that the base ‘B’ is sodium hydroxide (NaOH). It is a deliquescent substance and becomes sticky on absorbing moisture from atmosphere. It is commercially formed by the electrolysis of a strong solution of sodium chloride (brine).
It reacts with an acidic oxide such as CO2 or SO, gas to form corresponding salt and water. For example,
Question 47.
A sulphate salt of Group 2 element of the Periodic Table is a white, soft substance which can be moulded into different shapes by making its dough. When this compound is left in open for some time, it becomes a solid mass and cannot be used for moulding purposes. Identify the sulphate salt. Why does it show such a behaviour ? Give the reaction involved.
Answer:
The available information suggests that the element present in group 2 of the Periodic Table* is calcium (Ca) and the sulphate salt (white in colour) is Plaster of Paris. It can be moulded into different shapes by making its dough with water. When left in the open, Plaster of Paris changes into Gypsum which is a solid mass quite hard in nature and can no longer be used for moulding.
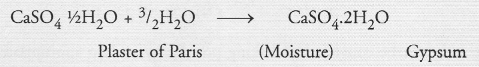
Question 48.
Identify the compound ‘Y’ on the basis of the reactions given below. Also write the name and chemical formulae of A, B and C.
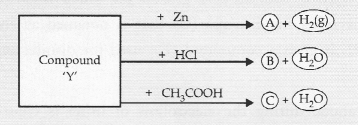
Answer:
The compound ‘Y’ is sodium hydroxide. It forms A, B and C as follows :
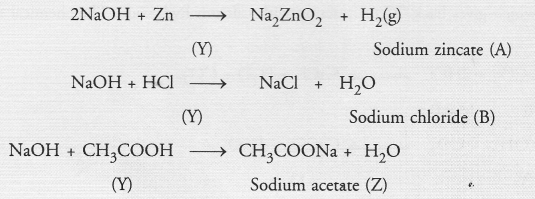
Acids, Bases and Salts – CBSE Class 10 Science – Extra Questions
Question-1
What is an acid?
Solution:
An acid is a hydrogen-containing chemical compound which, when dissolved in water, gives hydrogen ion (H+) or hydrated hydrogen ion (H2O. H+) or hydronium ion (H3O+).

Question-2
What are bases and alkalies?
Solution:
Oxides and hydroxides of metals and metal like radicals (e.g., NH4+ ions) are called bases. Bases ionise to give OH– ions in aqueous solution. Bases may be soluble or insoluble in water. The soluble bases are called alkalies. Thus all alkalies are bases but all bases are not alkalies.
Examples
NaOH and Cu (OH)2 both are bases, but, since NaOH is soluble in water, it is an alkali. On the other hand, since Cu (OH)2 is insoluble in water, it is not an alkali. Other examples of alkalies are KOH, Ca (OH)2 and NH4OH.
Question-3
Define pH.
Solution:
pH of a given solution is the negative logarithm to the base 10 of the hydrogen ion concentration, [H+] expressed in g ions/lit or moles/lit. Thus
pH=- log1- [H+].
Question-4
What are the practical applications of neutralisation reactions?
Solution:
Being alkaline in nature, cold milk is used to neutralise the acidity produced by HCl present in the gastric juice in the stomach.
Astronauts in space ships use this reaction to neutralise the dangerous levels of CO2.
Farmers add slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) to reduce acidity of soil.
Sting of ants and bees contains formic acid. This can be neutralised by rubbing soap, which contains free sodium hydroxide.
Persons suffering from acidity are given antacid tablets, containing magnesium hydroxide which neutralises excess HCl produced, in stomach. Alternately, they are advised to sip cold milk, which neutralises HCl.
Question-5
Why the salts solutions of strong acid and strong alkali are neutral?
Solution:
Let us take the example of potassium sulphate, which is a salt of strong acid [sulphuric acid] and strong base [potassium hydroxide solution].
From the above equation, it is clear that water is always feebly ionised and hence solution of potassium sulphate is neutral in nature.

Question-6
What is an universal indicator?
Solution:
Universal indicator is a solution, which undergoes several colour, changes over a wide range of pH. The colour is used to ‘indicate’ pH directly. Universal indicators are usually mixtures of several indicators.
Question-7
Why common indicators cannot determine pH value of a solution?
Solution:
Common indicators, such as litmus; methyl orange and phenolphthalein can easily tell, us whether a solution is acidic or alkaline, but they cannot easily tell how much a given acidic solution is stronger than another acidic solution. It means they cannot really tell us the pH value of different acidic or alkaline solutions.
In case of litmus, we cannot tell about pH values of 5,6 and 7. Similarly, in case of methyl orange pH values between 3 and 8 will not be very accurate.
Question-8
What are the general characteristics of acids?
Solution:
They have a sour taste
They turn blue litmus to red and methyl orange to red.
They react with active metals to give hydrogen
They decompose carbonates to produced carbon dioxide and water.

Question-9
What is called deliquescent? Give examples.
Solution:
Compounds that take up enough water from the air to dissolve in the water they have taken up are called deliquescent. Calcium chloride (CaCl2) and Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) are the examples of deliquescent.
Question-10
Write the uses of chlorines.
Solution:
Chlorine is used in the production of bleaching powder.
Chlorine is used for making solvents for dry cleaning.
Chlorine is used to sterilise drinking water supply, and the water in swimming pools.
It is used in the production of hydrochloric acid.
We hope given extra questions for class 10 science helpful to you. In case if you need any assistance, please comment below.
