NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce?
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Intext Questions
Page Number: 128
Question 1
What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
Answer:
DNA copying has following importance in reproduction:
- It maintains the characteristics of species.
- It maintains the continuity of life.
- From this, the characteristics and features of organisms are transformed to their progeny.
- It produces variations in organisms which is the basis of evolution of new species.
Question 2
Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual?
Answer:
The various populations of organisms interact with many types of ecological niches. This is important for them to survive in given conditions. In case of any damage caused to the ecological conditions of the population, the population gets adversely affected. The organisms which are able to survive, may reproduce to develop population which is adapted or suited to the varied conditions. Hence variation is beneficial to species, but not to the individuals.
Page Number: 133
Question 1
How is the process of pollination different from fertilisation ?
Answer:
| Binary fission | Multiple fission |
| 1. In this an organism divides into two similar organisms. | 1. In this an organism produces two or more organisms. |
| 2. A cyst or thick layer is not formed around the cell. | 2. A cyst or thick layer is formed around the cell. |
| It generally occurs in favourable conditions Example : Amoeba, paramecium |
3. It can take place in unfavourable conditions too. Example: Malarial parasite. |
Question 2
How will an organism be benefited if it reproduces through spores ?
Answer:
An organism is benefited by reproducing through the spores because spores are surrounded by a thick layer which protects them in adverse conditions. When the favourable conditions occur, these spores start to grow again. In this way they are successfully live in unfavourable conditions.
Question 3
Can you think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration ?
Answer:
In complex multicellular organisms, specialised cells make up tissues, tissue make up organs, organs make up organ systems and finally organ systems make up organisms. Since complex multicellular organisms have a very high degree of organisation in their body, they cannot be reproduced from their cut body parts by the process of regeneration.
For example, a dog is a complex multicellular organism which cannot be regenerated from its cut body part say, a cut tail. This is because the cells present in the cut tail of a dog cannot produce dog’s organs like heart brain, lungs, stomach, intestines and limbs, etc, needed for the making of a complete dog.
Question 4
Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants ?
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is practiced for growing such plants which usually do not produce seeds or produce non-viable seeds.
Question 5
Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction ?
Answer:
DNA copying is essential part of the process of reproduction so that the characteristics of the parent organisms are transmitted to its offspring and at the same time some occasional variations are also produced in the offspring. The changes in the copy of DNA provide an organism the capability to survive in changing conditions.
Page Number: 140
Question 1
How is the process of pollination different from fertilisation ?
Answer:
| Pollination | Fertilisation |
| 1. The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a stamen to the stigma of a carpel is called pollination. | 1. Fertilisation occurs when the male gamete present in pollen grain joins with the female gamete (or egg) present in ovule. |
| 2. It takes place by various pollinating agents. | 2. It takes place by natural or artificial means. |
Question 2
What is the role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland ?
Answer:
(i) Both seminal vesicle and prostate gland secretes fluids which forms a part of the semen. The fluid secreted from seminal vesicle forms 60% of semen while the fluid secreted from the prostate gland forms 30% of the semen. It makes the path smooth through which the sperms travel.
(ii) This fluid protects the sperms from the acids present in the urethra.
(iii) This fluid provides nutrition to sperms in the form of fructose, calcium and some enzymes.
Question 3
What are the changes seen in girls at the time of puberty ?
Answer:
The various changes occur in girls at puberty are :
- Hair grow under armpits and pubic region.
- Mammary glands (or breasts) develop and enlarge.
- The hips broaden.
- Extra fat is deposited in various parts of the body like hips and thighs.
- Fallopian tube, uterus and vagina enlarge.
- Ovaries start to release eggs.
- Menstruation (monthly periods) starts.
- Feelings and sexual drives associated with adulthood begin to develop.
Question 4
How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body ?
Answer:
In mother’s body, the embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood. For this, there is a special structure, called placenta. Placenta contains villi. There are empty spaces in mother’s tissues that cover the villi. It provides a large surface area for the transfer of glucose, oxygen and other substances from the mother to the embryo.
Question 5
A woman is using a copper-T. Will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases ?
Answer:
Copper-T is a contraceptive method which prevents implantation of the zygote inside the uterus. It cannot prevent a women from sexually transmitted diseases. These diseases are transmitted by contact which cannot be prevented by copper-T.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Textbook Chapter End Questions
Question 1
Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in
(a) amoeba
(b) yeast
(c) plasmodium
(d) leishmania
Answer:
(b) Yeast
Question 2
Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings ?
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopian tube
Answer:
(c) Vas deferens
Question 3
The anther contains
(a) sepals
(b) ovules
(c) carpel
(d) pollen grains
Answer:
(d) Pollen grains
Question 4
What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction ?
Answer:
(i) In asexual reproduction, the offspring are almost identical to their parent because they have the same genes as their parent. So, much genetic variation is not possible in asexual reproduction. This is a disadvantage because it inhibits the further evolution of the organism.
(ii) In sexual reproduction the offspring, although similar to their parents, are not identical to them or to one another. This is because the offspring receive some genes from the mother and some from the father. Because of the mixing of genes of mother and father in various different combinations, all of the offspring have genetic variations. In this way, sexual reproduction leads to a greater variety in population. This means that a species (animal or plant) can adapt quickly to changes in its surroundings. This is because there are always likely to be some individuals which are more suited to the changes than others, and these individuals will survive and reproduce themselves.
Question 5
What are the functions performed by the testis in human beings ?
Answer:
The functions of testes in humans are following :
(i) After the stage of adolescent, testes produce male gametes in the human males which are called sperms.
(ii) A hormone called testosterone is produced in testes. Testosterone controls the development of reproductive organs and secondary sexual characters.
Question 6
Why does menstruation occur ?
Answer:
If the ovum (or egg) does not get fertilised (due to non-availability of sperm in the female body) then the thick and soft inner lining of uterus is no longer needed and hence it breaks. So, the thick and soft inner lining of uterus alongwith the blood vessels and the dead ovum (or egg) comes out of the vagina in the form of blood called menstruation. Menstruation occurs after the interval of every 28 days and the time period between ovulation and menstruation is about 14 days.
Question 7
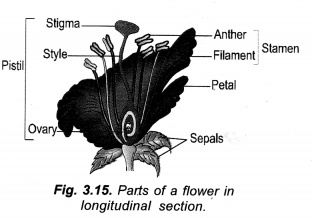
Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
Answer:
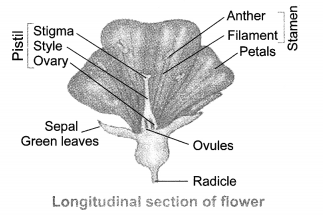
Question 8
What are the different methods of contraception ?
Answer:
The different methods of contraception are as follow :
(i) Barrier method : In this method, condom, diaphragm and cervical caps are used. These prevent the entry of sperms in the female genital tract during sexual intercourse.
(ii) Chemical method : In this method a woman uses two kinds of pills (oral and vaginal pills). The oral pills are hormonal preparations which suppress the release of ovum in fallopian tube. These are called oral contraceptives. The vaginal pills/ creams are spermicidal. The chemicals in these spermicidals kill the sperms during their journey in the vaginal tract.
(iii) Intrauterine contraceptive devices : Intrauterine contraceptive devices such as copper-T are placed safely in the uterus by a skilled doctor. It prevents the sperms to reach the uterus.
(iv) Surgical method : In this method, a small part of vas deferens of male and fallopian tube of female is cut or tied by surgery. It is called vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females.
Question 9
How are the modes for reproduction different in unicellular and multicellular organisms ?
Answer:
| Reproduction mode in unicellular organisms | Reproduction mode in multicellular organisms |
| (i) A sexual reproduction takes place in unicellular organisms. | (i) Sexual reproduction takes place in multicellular organisms. |
| (ii) Only one organism is required in this method. | (ii) A male and a female both are required in this method. |
| (iii) No special cells are present for reproduction. | (iii) Special cells are present for reproduction. |
| (iv) No special organs are present for reproduction. | (iv) Special organs are present for reproduction located at the fixed position in the body. |
Question 10
How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations of species ?
Answer:
The introduction of variations during reproduction provides stability to the populations of various species by preventing them from getting wiped out during adverse conditions. Reproduction also helps to generate copies of individuals which are suited to a particular environment.
Question 11
What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods ?
Answer:
The reasons for adopting contraceptive devices are as follow:
- To control the birth rate and prevent the increase in population.
- To reduce the adverse effects on mother’s body due to frequent pregnancy.
- To provide safety from sexually transmitted diseases.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce?
Reproduction: Reproduction in animals and plants (asexual) and (sexual) reproductive health – need and methods of family planning. Safe sex vs HIV/ AIDS. Child bearing and women’s health.
Page 128
Question 1.
What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
Answer:
DNA copying in reproduction is important for maintenance of body designs and features. Moreover, DNA copying leads to variations. Variation is useful for the survival of species.
Question 2.
Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual?
Answer:
Population of organisms reside in well-defined places or niches in the ecosystem. However, niches can change because of reasons beyond the control of the organisms, e.g., temperature changes, water level changes, etc. If population of reproducing organisms suited to particular niche and if the niche is drastically altered, the population can be wiped out. However, if some variations are present in a few inAividuals in these populations, there will be chances for their survival. The surviving individual can further reproduce and develop a population according to the changed niche, Thus, variation is beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual.
Page 133:
Question 1.
How does binary fission differ from multiple fission ?
Answer:
When two new daughter cells are formed as a result of fission. It is called binary fission, e.g., Amoeba.When many daughter cells are formed as a result of fission, this is called multiple fission, e.g., Malarial parasite.
Question 2.
How will an organism be benefited if it reproduces through spores?
Answer:
Spore formation is an asexual mode of reproduction. Spores formed are covered by
thick walls that protect them from adverse conditions. During favourable condition thick resistant wall breaks down and new organism grows from it.
Spores are very light weight and they easily get dispersed through winds which give them more variations and thus better chances of survival.
Question 3.
Can you think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration?
Answer:
Complex organisms are not simply a random collection of cells where sPecialized cells are organised as tissues, and tissues ale organised into organs which then have to be placed at definite positions in the body. In such a carefully organised situation, it is not easy to develoP organism through regeneration
Question 4.
Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some type of plants?
Answer:
Vegetative propagation makes possible for the propagation of plants such as banana, orange, rose and jasmine that have lo6t the capacity to Produce seeds. Moreover, all plants produced through vegetative propagation are genetically similar to the parent plant.
Question 5.
Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
Answer:
The process of reproduction results in the production of off springs which resemble to their parents. This means during the reproduction there must be a transfer of the blueprint of the body design from parent to the off springs. As we know DNA contains all the information that passes from parents to the next generation, so before reproduction, DNA is copied in the parent cell. Out of these two copies, one copy is passed to the newly formed individual.
Page 140
Question 1.
How is the process Of pollination different from fertilization ?
Answer:
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma Of a flower whereas fertilization is the fusion Of male gamete with female gamete (egg).
Question 2.
What is the role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland ?
Answer:
Seminal vesicles and the prostate gland add their secretions so that the sperms are in a fluid (semen) which makes their transport easier and this fluid also provides nutrition.
Question 3.
What are the changes seen in girls at the time Of puberty ?
Answer:
Changes seen in girls at the time of puberty are :
1. Breast size begins to increase.
2. Girls begin to menstruate.
3.Growth Of pubic hair.
4.Skin becomes oily.
Question 4.
How does the embryo get nourishment inside the Mother’s body?
Answer:
embryo gets nutrition from mother’s blood with the help Of a special tissue called placenta. Through placenta, glucose and oxygen pass from mother to the embryo. Moreover, waste substance of embryo are removed through placenta into the
mother’s blood.
Question 5.
If a woman is using a copper-T will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer:
No, copper-Twill not protect her from Only Barrier methods protect from sexually transmitted diseases.
Page 141
Question 1.
Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in :
(a) Amoeba
(b) Yeast
(c) Plasmodium
(d) Leishmania.
Answer:
(b) Yeast.
Question 2.
Which of the following is not a pan Of the female reproductive system in human beings ?
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopian tube
Answer:
(c) Vas deferens.
Question 3.
The anther contains :
(a) Sepals
(b) Ovules
(c) Carpel
(d) Pollen grains.
Answer:
(d) Pollen grains
Question 4.
What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction leads to new combination Of genes as it involves two parents and meiosis. This produces variation in offspring. Variations are the basis for evolution.
Question 5.
What are the functions performed by the testes in human beings?
Answer:
Functions Of testes are .
(i) Testes produce sperms.
(ii) Testosterone (male sex hormone) is also produced by testes.
Question 6.
Why does menstruation occur?
Answer:
If the egg is not fertilized and uterus does not get zygote, the developed lining slowly breaks and menstruation occur.
Question 7.
What are the different methods of contraception?
Answer:
There are three main methods of contraception :
- Barrier methods,
- Chemical methods, and
- Surgical methods.
1. Barrier methods: In barrier methods, physical devices such as condom, diaphragm and cervical caps are used. They prevent the entry Of sperms in the female genital tract during copulation.
2. Chemical methods: The chemical methods make use of specific drugs by females. There are two types of such drugs, Oral pills and vaginal pills. Oral pills are mainly hormonal preparation, and are called oral contraceptives (OCS).
3. Surgical methods: In the surgical methods, a small portion of vas deferens in male, and the fallopian tube in female, in surgically removed or ligated (tied). It is called vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females.
Apart from these three methods the intrauterine contraceptive devices are used to prevent pregnancies. The use of Intra Uterine Contraceptive Devices (IUCDs) is also very effective and popular. A copper-T is placed safely inside the uterus by a practising doctor or a skilled nurse. IUCDs prevent implantation in the uterus.
Question 8.
How are the modes for reproduction different in unicellular and multicellular organisms ?
Answer:
Unicellular organisms reproduce asexually whereas multicellular organisms reproduce manly by n 1 reproduction.
Question 9.
How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations Of species?
Answer:
The rate Of birth and death in a given population determine its stability. The rate of birth should be approximately equal to the rate of death. So, by checking birth rate, which is increasing at an alarming rate, stability to population of species can be provided
Question 10.
What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods?
Answer:
Frequent pregnancies have an adverse effect on the health of a woman. Frequent and unwanted pregnancies can be avoided by adopting contraceptive methods. Also, these methods check population growth by controlling child birth rate.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) [1 Mark each]
Question 1.
Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in [NCERT]
(a) Amoeba
(b) Yeast
(c) Plasmodium
(d) Leishmania
Answer:
(b) Asexual reproduction in Hydra and yeast takes place by budding.
Question 2.
The ability of a cell to divide into several cells during reproduction in Plasmodium is called [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) budding
(b) reduction division
(c) binary fission
(d) multiple fission
Answer:
(d) Multiple fission Organisms divide into many daughter cells simultaneously, e.g. Plasmodium.
Question 3.
The anther contains [NCERT]
(a) sepals
(b) ovules
(c) carpels
(d) pollen grains
Answer:
(d) Anther is the male reproductive part in plants. It contains pollen grains, having male germ cells.
Question 4.
Characters that are transmitted from parents to offspring during reproduction show [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) only similarities with parents
(b) only variations with parents
(c) both similarities and variations with parents
(d) neither similarities nor variations
Answer:
(c) In sexual reproduction, the offsprings are not exactly identical to the parents or to one another. This is because the offsprings receive some genes from mother and some from father. Because of mixing of genes on re-establishment of the exact number of chromosomes as in the parents, the offsprings show both similarities and variations with their parents.
Question 5.
Which among the following diseases is not sexually transmitted? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Syphilis
b) Hepatitis
(c) HIV-AIDS
(d) Gonorrhoea
Answer:
(b) The diseases, which are spread by sexual contact with an infected person are called Sexually Transmitted Diseases or STDs, e.g. gonorrhoea, syphilis and AIDS. Hepatitis is a water borne viral disease which affects liver.
Question 6.
Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings? [NCERT]
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopian tube
Answer:
(c) Vas deferens is a part of male reproductive system in humans.
Question 7.
A feature of reproduction that is common to Amoeba, Spirogyra and yeast is that [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) they reproduce asexualiy
(b) they are all unicellular
(c) they reproduce only sexually
(d) they are all multicellular
Answer:
(a) Amoeba and yeast are unicellular while Spirogyra is multicellular. But, all the three reproduce asexualiy.
Question 8.
Which among the following statements are true for unisexual flowers? [NCERT Exemplar]
I. They possess both stamen and pistil.
II. They possess either stamen or pistil.
III. They exhibit cross-pollination.
IV. Unisexual flowers possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits.
(a) I and IV
(b) II, III and IV
(c) III and IV
(d) I, III and IV
Answer:
(b) The flowers which are unisexual (papaya, watermelon) contain either stamens or carpels. Since, only one reproductive organ is present in them, they depend on cross-pollination to form zygote after fertilisation. Both stamens and carpels are required for fertilisation, so only one of them cannot produce fruits.
Question 9.
Length of pollen tube depends on the distance between [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) pollen grain and upper surface of stigma.
(b) pollen grain on upper surface of stigma and ovule.
(c) pollen grain in anther and upper surface of stigma.
(d) upper surface of stigma and lower part of style.
Answer:
(b) Length of pollen tube depends on the distance between pollen grain on upper surface of stigma and ovule. A pollen grain falls on the stigma of the carpel, bursts open and develops a pollen tube downwards through the style towards the ovule in the ovary.
Question 10.
Which among the following statements arer true for sexual reproduction in flowering plants? [NCERT Exemplar]
I. It requires two types of gametes.
II. Fertilisation is a compulsory event.
III. It always results in formation of zygote.
IV. Offsprings formed are clones.
(a) I and IV
(b) I and II
(c) I, II and III
(d) I, II and IV
Answer:
(c) Sexual reproduction creates variation in organisms, so, clones cannot be produced through it. Clones are identical copy of parent organism. Sexual reproduction needs two type of gametes, i.e. male and female to form zygote after fertilisation.
Question 11.
Factors responsible for the rapid spread of bread mould on slices of bread are [NCERT Exemplar]
I. large number of spores.
II. availability of moisture and nutrients in bread.
III. presence of tubular branched hyphae.
IV formation of round-shaped sporangia
(a) I and III
(b) II and IV
(c) I and II
(d) III and IV
Answer:
(c) Under favourable Conditions (like damp and warm conditions, availability of nutrients), the fungal spores present in the air, lands on food, germinate and produce new plaints.
Question 12.
During adolescence various changes occur in the body of humans. Mark one change associated with sexual maturation in males. [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Loss of milk teeth
(b) Increase in body height
(c) Cracking of voice
(d) Weight gain
Answer:
(c) Hypertrophy of larynx results in low pitched. cracking voice in human males during adolescence.
Question 13.
Observe the diagram given along side.
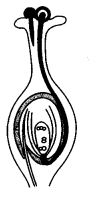
What happens after the above stage?
(a) The ovary splits open
(b) Ovary develops into a fruit and ovules into seeds
(c) The pvules are dispersed
(d) Germination of seeds takes place
Answer:
(b) Ovary develops into a fruit and ovulesdnto seeds as in the above given diagram fertilisation has already taken place.
Question 14.
What in your opinion could be the best reason to explain why menstruation is not taking place in a healthy woman?
(a) Early release of ovum
(b) Psychological reason
(c) Fertilisation of ovum
(d) Build up of female sex hormones in the blood stream
Answer:
(c) If a woman is not having her menstruation on time the probable reason from the given option is that fertilisation of ovum has taken place. Because, during gestation period of pregnancy, menstruation does not take place.
Question 15.
The correct sequence of reproductive stages seen in flowering plants is [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) gametes, zygote, embryo, seedling
(b) zygote, gametes, embryo, seedling
(c) seedling, embryo, zygote, gametes
(d) gametes, embryo, zygote, seedling
Answer:
(a) Correct sequence of reproductive stages in flowering plants is → formation of gametes → fusion of gametes to form zygote → zygote develops into embryo in the ovary → ovule develops a tough coat and converts into a seed.
Question 16.
Offsprings formed by asexual method of reproduction have greater similarity among themselves because [NCERT Exemplar]
I. asexual reproduction involves only one parent.
II. asexual reproduction does not involve gametes.
III. asexual reproduction occurs before sexual reproduction.
IV. asexual reproduction occurs after sexual reproduction.
(a) I and II
(b) I and III
(c) II and IV
(d) III and IV
Answer:
(a) Offsprings have greater similarity as only one parent is involved in asexual reproduction thus, no gametes are formed.
Question 17.
Two flowers are identified by a botanist with the following features that flower A is having only stamen and flower B is having both stamen and pistil. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Flower A will bear seeds and flower B cannot bear seeds after fertilisation.
(b) Flower A will produce pollen grains and flower B cannot produce pollen grains.
(c) Flower A cannot be fertilised and flower B can show fertilisation.
(d) Neither flower A and nor flower B can show self-pollination.
Answer:
Option (c) is correct. Since, flower A bears only stamen, i.e. male reproductive part so, it cannot get fertilised. And flower B bears both male and female reproductive parts, therefore it can get fertilised by pollination and can change into fruit.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce
Asexual Reproduction
- It involves only one parent.
- There is no formation and fusion of gametes.
- The young ones formed are almost identical to each other as well as to the parent cell.
- Asexual reproduction generally occurs during favourable environmental conditions and when there is an abundance of food.
- It is a faster method of reproduction.
Types of Asexual Reproduction is Unicellular Organism
(i) Binary Fission: Seen in bacteria, protozoa like Amoeba, Paramecium. (In these first pseudopodia withdrawn (karyokinesis) the nucleus of the parent cell divides and then the cytoplasm divides (cytokinesis) resulting in the formation of two daughter cells). It occurs during highly favourable conditions. The cell division can occur in any plane as in case of Amoeba. However, organisms like Leishmania. (cause Kala-azar), which have a whip like flagella at one end, binary fission occurs in a definite orientation in relation to the flagellum.

Cytokinesis: Division of cytoplasm.
Karyokinesis: Division of Nucleus.
(ii) Multiple Fission: Seen in Plasmodium, (a malarial parasite). In this during unfavourable conditions, the parent cell develops a thick resistant wall around itself forming a cyst. Within the wall, the cytoplasm divides many times to form many plasmodia. When conditions become favourable, the cyst wall breaks and the Plasmodium are released.

(iii) Budding: Seen in Yeast (a fungus). The parent yeast cell develops a protrusion or an outgrowth at its upper end. The nucleus of the parent cell divides and one of them moves into the outgrowth which grows bigger and finally separates from the parent cell to lead an independent existence. Very often if the conditions are highly favourable, a chain of buds is formed.

Types of Asexual Reproduction in Multicellular Organisms :
(i) Fragmentation: Seen in multicellular organisms which have a relatively simple body organisation like Spirogyra. Spirogyra has a filamentous body. (If it breaks into smaller pieces or fragments). Each fragment has the capacity to form a new individual.
However, all multicellular organisms cannot show cell-by-cell division as cells from tissues which form organs. These organs are placed at definite positions in the body. Hence, they need to use more complex methods of reproduction.

(ii) Regeneration: It is the ability of organisms to develop their lost parts. Some organisms show have high regenerative capacity it is also a means of reproduction for example; Planaria. (Regeneration is carried out by specialized cells which redivide to form a mass of cells from which different cells undergo changes to become different cell types and tissues. These changes occur in an organized sequence known as development).

(iii) Budding: Seen in Hydra. Parent Hydra develops a bud at its lower end. This grows in size and finally breaks off to live independently.

(iv) Spore Formation: Seen in Rhizopus (a fungus). Rhizopus body is made up of thread-like structures called hyphae. The erect hyphae bear sporangia inside which reproductive structures called spores are formed. Spores are asexually reproducing bodies having a thick protective wall. They are produced during unfavourable times and help to tide over the unfavourable environmental conditions. When the spores fall on a suitable medium, each one forms a new individual.

(v) Vegetative Propagation: Method by which plants reproduce by their vegetative parts such as roots, stems, and leaves.
Types of Vegetative Propagation: It is two types
- Natural vegetative propagation.
- Artificial vegetative propagation (Tissue culture).
Mint reproduces naturally by roots. Sugarcane, jasmine by stems and Biyophyllum by leaves. In biyophyllum buds are produced in the notches along the leaf margins and when they fall on the soil, they develop into new plants.

Importance of Vegetative Propagation
- Plants can bear flowers and fruits earlier.
- Plants which have lost the ability to produce viable seeds can also reproduce by vegetative propagation.
- All plants are genetically almost similar to the parent plant.
- Seedless varieties can be obtained.
- The property of vegetative propagation is used by horticulturists in developing methods like layering, grafting to grow many plants like sugarcane, roses, or grapes.
Tissue Culture: The technique of developing new plants from a cell or tissue in a nutrient medium under aseptic conditions. The cell or tissue is placed in a nutrient medium where it forms a mass of cells called callus. This callus is then transferred to another nutrient medium where it differentiates and forms a new plant.
Sexual Reproduction: Sexual reproduction in plants, Sexual reproduction in human beings. The mode of reproduction that takes place with the involvement of two individuals of two different sexes i.e. male and female.
During sexual reproduction, male organism having male sex organs produces male gametes i.e. sperms which are small and motile and the female organism having female sex organs produces ova which are generally large and store food. Male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote that grows into a new organism.
Significance of Sexual Reproduction :
- Sexual reproduction involves DNA as well as cellular apparatus of two different organisms which promotes diversity of characters in the offspring.
- Since gametes are derived from two different organisms, it results in a new combination of genes which increases the chances of genetic variations.
- Sexual reproduction results in the origin of. new species.
- Sexual reproduction involves division in the sex organs that reduces the DNA matter to half so that the zygote formed after fusion has the same amount of DNA as the parents it maintains DNA in a species.
Limitation of Sexual Reproduction: Sexual reproduction involves the process of combining DNA from two different organisms which may bring some undesirable features also.
Sexual reproduction in flowering plants
- The reproductive parts are present in the flower.
- The parts of the flower are sepals, petals, stamens and carpels.
- Sepals are green structures that protect the inner parts when the flower is in bud stage.
- Petals are colourful and attract the insects for pollination.
- Stamens are male reproductive parts and produce pollen grains that contain male gametes. Each stamen has two parts—
- Filament i.e. stalk and Anther i.e. swollen top part which has large number of pollen grains.

The carpel is the female reproductive part and produces ovules that contain female gametes. It has three parts—Stigma which is top sticky part and receives pollen grains during pollination. Style which is the middle long part and ovary which is the swollen part and contains ovules. Each ovule has an egg cell i.e. female gamete.

The flowers may be bisexual i.e. having both stamens and carpels for example; Mustard China Rose (Hibiscus).
The flower may be unisexual i.e. paving either stamens or carpels for example; Papaya, Watermelon.
Pollination: The process of transfer of pollen grains from an anther to the stigma of the flower is pollination. Two types of pollination are:
(i) Self-pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or another flower of the same plant.
(ii) Cross-pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of another flower or another flower of a different plant of the same species. It generally takes place with the help of some agents like insects, birds, wind and water.

Fertilization: Fertilization is the process of fusion of male and female gamete to form a zygote during sexual reproduction. Pollination is followed by fertilisation in plants. The events are
Pollen grains land on the stigma of the ovary.
Pollen tubes grow out of the pollen grains, travel through the style and reach the ovary, through micro pyle.
Pollen tube has two male germ cells. Each ovule has two polar nuclei and a female germ cell (egg).
Pollen tube releases two male germ cells inside the ovule, one of them fuses with female germ cell and forms a zygote which grows into the baby plant i.e. embryo, the fusion is known as syngamy. The other male germ cell fuses with two polar nuclei, the process is known as triple fusion. So in flowering plants two fusions take place during fertilisation. It is called double fertilisation.

Post-fertilisation changes: After fertilisation the following changes takes place in the flower.
Zygote divides several times and forms an embryo inside the ovule.
- The ovule develops a tough coat and changes into the seed.
- The ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form a fruit.
- Petals, sepals, stamens, style and stigma shrivel and fall off.
Seed and its parts: The advantage of seed is that it protects the future plant i.e. embryo.
Seed has two parts: Cotyledons and Embryo Cotyledons store food for the future plant.
Embryo has two parts: plumule and radicle. Plumule develops into shoot and radicle develops into root.
The process of development of a seedling from the embryo under appropriate conditions is known as germination.

Reproduction in Human Being: Human beings show sexual reproduction. Male parent produces male gametes called sperms. Female parent produces female gametes called ova. Sperms have tail and are therefore, motile. They are produced in large numbers in the testes. Ovum is bigger, non-motile and only one ovary produces one ovum in one month. There is no food stored in the sperms whereas ova contain stored food. Both the gametes are microscopic unicellular and have half the number of chromosomes as compared to the body cells.
Human beings become reproductively active from the onset of puberty. Puberty is the period during adolescence when the rate of general body growth begins to slow down and reproductive tissues begin to mature. Onset of puberty in human males is between 11 to 13 yrs of age, while in human females is between 10 to 12 yrs. of age. Puberty is associated with many physical, mental, emotional and psychological changes in boys and girls which occur slowly over a period of time. These are called secondary sexual characters. For instance thick dark hair start growing in new parts of the body such as arm pits and genital area between the thighs. Thinner hair appear on legs, arms and face. Skin becomes oily and pimples may appear on the face. Individuals become more conscious of their bodies become more independent, more aggressive etc.
In case of boys beard and mustache start appearing, voice begins to crack, reproductive organs develop and start producing releasing sperms.
In case of girls, breast size begins to increase, skin of the nipples darkens, menstruation starts.
The act of mating between the male and female partner is termed as copulation.
Male Reproductive System: Male reproductive system consists of the following components

- 1 pair of testes
- A system of ducts
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens or the sperm duct
- Urethra
- A system of glands
- Seminal vesicles
- Prostrate gland
- Cowper’s gland
- A copulatory organ called a penis.
One pair of testes are present in a bag-like structure called scrotum which lies outside the abdominal cavity, hence they are extra abdominal in position. This is so because the testes have to be maintained at 1-3 degree lesser temperature than the body in order to produce functional sperms.
Functions of testes
- To produce male gametes i.e. the sperms.
- To produce a male reproductive hormone called testosterone which is responsible for producing sperms as well as secondary sexual characteristics in males.
Attached to each testis is a highly coiled tube called epididymis. The sperms are stored here and they mature in the epididymis.
Each epididymis leads into the sperm duct or the vas-deferens. Each vas-deferens rises up and enters into the abdominal cavity. It unites with the duct coming from the urinary bladder to form a common duct called urethra which passes through the penis and opens to the outside. Along the way the ducts of the three glands also open and pour their secretions into the vas deferens.
Function of the vas-deferens: It is meant for the passage of the sperms in the male body.
Functions of the glands: They produce different secretions which provide nutrition as well as medium for locomotion to the sperms.
The secretions of the three glands along with the sperms is known as semen.
Function of the urethra: It is the common passage for both semen and urine from the body to. the outside.
Penis: It is the organ which is used to introduce semen into the female body. It is richly supplied with blood vessels.
Female Reproductive System: It consists of the following components

- 1 pair of ovaries
- 1 pair of fallopian tubes or oviducts
- A uterus/womb
- A vagina/birth canal.
Each ovary is almond shaped and present inside the abdominal cavity. At the time of birth each girl child already contains thousands of immature ova. These ova start maturing only from the time of puberty. Only one ovum is produced by one ovary in one month and each ovary releases an ovum in alternate months. The release of an ovum from the ovary into the abdominal cavity is known as ovulation.
Functions of ovary
- To produce and release ova
- To produce female reproductive hormones: estrogen and progesterone.
There are two fallopian tubes. The end lying close to the ovary has finger like structures called fimbriae. The two fallopian tubes unite to form an elastic bag like structure called uterus.
Function of the fallopian tubes: It is the site of fertilization between the male and the female gametes and formation of the zygote early embryo.
The inner lining of the uterus is richly supplied with blood vessels and is known as endometrium. The narrow end of the uterus is called cervix.
Function of the uterus: The embryo formed in the fallopian tube comes down and gets attached to the endometrium (implantation) and develops for the next nine months till the baby is delivered.
Vagina: The uterus opens into the vagina through the cervix. The vagina is a muscular tube through which the baby is delivered at the end of nine months. It also serves as the canal for receiving the semen at the time of copulation.
The semen is discharged into the vaginal tract during copulation. The sperms travel upwards and reach the fallopian tube where one sperm fuses with the ovum to form the zygote. The zygote divides and redivides as it descends into the uterus and the embryo gets implanted in the endometrium. The endometrium thickens so as to receive the embryo.
The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta, which is a disk-like structure embeded in the uterine wall. It contains finger-like villi on the embryo side, while on the mother’s side blood spaces surround the villi. Villi provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother to the developing embryo and the wastes to pass from the embryo to the mother through the placenta. When the embryo starts resembling a human is formed, it is termed as a foetus. The foetus continues
to develop inside the uterus for almost nine months after which the baby is delivered as a result of rhythmic contractions of the uterine muscles.
Menstruation: It is the loss of blood, mucous along with the unfertilized ovum and the ruptured cells and tissues of the endometrium through the vagina of the female. It is a 28-day cycle which occurs in every reproductively active female (from puberty). The flow of blood continues for 2 to 8 days. If the ovum does not get fertilized, then the endometrium starts sloughing off and there is loss of blood and mucous etc. through the vagina. In case the ovum gets fertilized, then the endometrium becomes thick and spongy for nourishing the embryo and hence menstruation does not occur. A lady with a developing embryo in her womb is termed as pregnant. The beginning of menstruation at puberty is known as menarche. The stopage of menstruation when the woman is 45-55 yrs of age is called menopause.
Reproductive Health: Sexually transmitted diseases and birth control.
A number of diseases occur as a result of sexual intercourse if one of the partners is infected. These are known as sexually transmitted diseases (STD’s). They can be caused by bacteria for example; syphilis, gonorrhoea; or caused by a virus for example; HIV-AIDS, warts etc. The transmission of these diseases can be avoided by using birth control measures such as wearing a condom during the sexual act.
Birth control measures: They can be mechanical, chemical and surgical.
Mechanical methods: These are used to prevent the passage of semen to the follopian tube :
(i) Use of condoms: Condoms are thin rubber tubes worn over the penis before sexual intercourse. The semen gets collected in this and is not discharged into the vagina.
(ii) Diaphragm: It is a thin rubber fixed over a flexible metal ring which is fitted over the cervix in a woman’s body by a doctor.
(iii) Intra Uterine Contraceptive Device (IUCD) or loop: It is inserted in the uterus and its insertion causes certain secretion which prevents the implantation of the embryo in the uterine wall.
Both methods (ii) and (iii) cause side effects.

Chemical methods
- Use of spermicides: These are strong sperm-killing chemicals available in the form of creams, jellies etc. which are injected into the vagina just before copulation.
- Oral contraceptive pills: These are hormonal pills which prevent ovulation but do not stop menstruation.
Surgical methods
- Vasectomy: It involves cutting and ligating the vas deferens in males.
- Tubectomy: It involves cutting and ligating Reproductive organs the fallopian tubes in females.
- Medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) or abortions is carried out to eliminate the developing embryo. This practice can, however, be misused to carry out female foeticide which involves the killing of the female foetus. It should be avoided at all cost as it disturbs the male-female ratio in a population.
Reproduction: It is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves.
- Reproduction ensured continuity of life on earth.
- It is a bridge to hereditary transmission.
- It involves a continuation of characters from the parents to daughter cells by copying of DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) molecules present in the chromosomes of the cell.
- Copying of DNAs is also not a foolproof exercise, even minute changes bring about variation in the blue print of the offsprings.
- The useful variations are retained while the harmful ones do not go beyond.
- Actually, variations help the species to withstand drastic environmental changes, thus save the species from becoming extinct and promotes its survival for a longer time.
- This inbuilt tendency of variation is the “basis” for Evolution.
Asexual Reproduction: It is extremely useful as a means of rapid multiplication. It is common in lower plants and animals.
Different forms of Asexual Reproduction:
- Fission: The parent cell divides/splits into two daughter cells —Binary fission and splits into many cells —Multiple fission.
- Budding: A new organism is produced as an outgrowth of the parent body part.
- Spore Formation: Spores are small, the bulb-like structure which develops at the top of the erect hyphae of the fungus-plant, when released into the air germinate, into new individuals after landing into food or soil.
- Fragmentation: It is the accidental process when the broken pieces of an organism (fragments) grows into a complete organism. Example, fragmentation in Spirogyra.
- Regeneration: When simple animals like a hydra, planaria develop a new individual from their broken older part it is known as regeneration. It is carried out by specialised cells which grow large numbers of cells.
Vegetative Propagation: A mode of reproduction in which parts like the stem, root, leaves develop into new plants under favourable conditions.
Benefits:
- Plants can bear flowers, fruits more quickly than those produced from seeds.
- Growing banana, orange, rose, jasmine that have lost the capacity to produce seeds.
- The genetical similarity is maintained in the plants. Example, sugarcane, rose, grapes by layering or grafting.
Sexual Reproduction: When reproduction takes place as a result of the fusion between two gametes, one from each parent, it is called sexual reproduction.
- This process of fusion between two gametes is called fertilization.
- The formation of gametes involves an exchange of chromosomal (genetic) fragments between homologous chromosomes causing genetic recombination which leads to variation.
Sexual Reproduction in Plants: It occurs mostly in flowering plants.’ In fact, flowers are the reproductive organ of plants.
- Pollen grains of a flower transfer to the stigma of the carpel of the same flower (Self-Pollination) or to the carpel of another flower (Cross-Pollination).
- This transfer of pollens is achieved by agents like wind, water or animals. After pollination, the pollen grains reach the egg cell in the form of a pollen tube.
- Fertilization. The fusion between the pollen grain and female egg cell. It occurs inside the ovary. The zygote is produced in this process.
- The zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a rough coat and is converted into a seed.
- Ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form fruit, while the seed contains the future plant or embryo which develops into a seedling under suitable conditions. This process is known as Germination.
Reproduction in Human Beings:
- Humans use a sexual mode of reproduction.
- It needs sexual maturation which includes the creation of the germ cells, i.e., egg (ova) in the female and sperm in the male partner and this period of sexual maturation is called Puberty.
- Human beings have a well-developed male and female reproductive system.
- The formation of the male germ cell (sperms) takes place in the testes (male reproductive organ). Actually, a pair of testes are located inside scrotum situated outside the abdominal cavity. It is meant to keep a relatively low temperature needed for the production of sperms by testes. Testes release a male sex hormone called testosterone whose function is to:
- regulate the production of sperms;
- brings about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty; and
- the sperms along with the secretion of the prostate gland and seminal vesicle, together constitute semen, which is released and made to enter into the female genital tract during Copulation.
Female Reproduction System:
- The female germ cells or eggs are made in the ovaries, a pair of which is located in both sides of the abdomen.
- When a girl is bom, the ovaries already contain thousands of immature eggs. At the time of puberty, some of these eggs start maturing. One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries.
- The egg is carried from the ovary to the womb through a fallopian tube. These two fallopian tubes unite into an elastic bag like structure known as the uterus.
- The uterus opens into the vagina through the cervix.
- Fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube of the female genital tract.
- The fertilized egg also called zygote gets implanted in the lining of the uterus, and starts dividing. The uterus is richly supplied with blood to nourish the growing embryo.
- If the zygote is not formed, the inner wall of uterus breaks which causes bleeding through vagina. This process is called Menstruation. It occurs at a regular interval of 28 days.
- The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called Placenta.
- Placenta provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother to the embryo. Similarly the wastes from developing embryo are removed to mother’s blood through placenta.
- The child is bom as a result of rhythmic contractions of the muscles in the uterus after nine months (36 weeks) of development inside the mother’s womb, called Gestation Period.
- The sexual cycle in a woman continues upto the age of 45 to 50 years. After that the ovaries do not release eggs. This stage is called Menopause. It also marks the end of menstruation in the woman.
Reproductive Health: Reproductive health means total well-being in all aspects of reproduction, z.e., physical, emotional, social and behavioural.
Contraception: It is the avoidance of pregnancy through different methods—Natural methods, Barrier method, Oral contraceptives, Surgical methods.
Advantages of contraception: Help in birth control, prevent sexually transmitted diseases, prevent unwanted pregnancies, keep population explosion in check.
1. Reproduction is the process by which a living organism is able to produce new individuals of its own kind. Unlike other life processes such as nutrition, respiration, etc., it is not essential to, maintain the life of an individual organism. But it is important for the existence and continuity of the species.
2. Reproduction involves the creation of DNA copy and additional cellular apparatus by the cell involved in the process.
3. The process of DNA copying leads to variations. This inbuilt tendency for variations during reproduction is the basis for evolution.
4. Living organisms’ reproduce mainly through :
- Asexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction
5. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
(a) Single ceiled organisms reproduce through following ways:

(ii) Budding (also by multicellular organisms)
(iii) Spore formation (also by multicellular organisms)
(b) Asexual reproduction by multicellular organisms:
(i) Fragmentation and Regeneration

6. Fission: In unicellular organisms when cell becomes fully mature, it splits into two or more parts. It is called the fission. In organisms such as Amoeba, splitting can take place in any plane. But in organisms like Leishmania, having whip like structure at one end of the cell, binary fission occurs in a definite orientation in relation to these structures.


7. Regeneration : It is the ability to give rise to new organism. When the individual is cut or broken up into many pieces. It can be seen in Hydra and Planaria and is known as regeneration.
Regeneration is carried out by specialised cells. These cells proliferate and rqgkeJarge numbers of cells. From this mass of cells, different cells undergo changes to become various cell types and tissues. These changes take place in an organised sequence referred to as ” development. However, regeneration is not the same as reproduction, since most organisms would not normally depend on being cut up to be able to reproduce.

8. Budding: Organisms such as Hydra use regenerative cells for reproduction in the process of budding. In Hydra, a bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at one specific site. These buds develop into tiny individuals and when fully mature, detach from the parent body and become new independent individuals.

9. Spore Formation (Sporulation): Some bacteria and lower organisms make spores. During spore formation, knob like structure called sporangium develops from the fungal hypha. Sporangia contain spores that eventually develop into new individual. The spores are covered by thick walls that protect them until they come in contact with moist surface or substratum and can begin to grow.

10. Fragmentation : It can be seen in Spirogyra. During this process filament of spirogyra simply breaks up into smaller pieces upon maturation. These pieces or fragments grow into new individuals. This process occurs under favourable conditions of moisture, temperature, light and nutrient availability.
11. Vegetative propagation: It is the simplest method of reproduction in some higher plants in which new plant is produced from any vegetative part of the plant such as root, stem, leaf, etc.
Advantages of vegetative propagation : Vegetative propagation is useful for plants those have lost the capacity to produce seeds, e.g. banana, rose, jasmine. Moreover, all plants produced are genetically similar to the parent plant.
Natural Vegetative Propagation: In some plants like guava, sweet potato, dahlia, roots sprout and grow into new plants during favourable conditions. In some other,stems grow horizontally and develop root below and leaves above the ground. Many other common examples of vegetatively propagating plants are onion, banana, garlic, ginger, turmeric, bryophyllum and water hyacinth.
12. Vegetative propagation in Bryophyllum: Bryophyllum reproduces by the vegetative propagation method. During this method, buds produced in the notches along the leaf margin of bryophyllum fall on the soil and develop into new plants.

13. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION :
Sexual reproduction involves two individuals for producing a new individual. Sexual reproduction begins with fertilization, which is defined as the union of two different gametes. The motile germ-cell fptrUeh or sperm) is called the male gamete and germ-cell containing stored food (egg or ovum) is called the female gamete. The process of fusion of two gametes is called fertilization. After fertilization, a zygote is formed , which develops into a new organism.

14. Sexual reproduction in Plants : The flowering plants or angiosperms bear special reproductive parts located in the flower. Various parts of flower are; sepals, petals, stamens and carpels.
Most flowers have both male and female reproductive organs. The flower may be unisexual (papaya, watermelon) when it contains either stamen or carpel or bisexual (Hibiscus, Mustard) when it contains both stamens and carpels. It has male reproductive part cal led stamen and a female reproductive part called carpel. Carpel is made of three parts. The swollen bottom part is the ovary, middle elongated part is the style and the terminal part which may be sticky is the stigma.
The ovary contains ovules and each ovule has an egg cell. Each stamen consists of stalk called filament, and a flattened fertile top called anther. The anthers produce the pollen grains. The pollen grains produce male gametes which fuse with (egg cel I) female gamete present in the ovule. This fusion of the germ-cells or fertilization gives zygote which grows into a new plant. Pollination: It is the process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of flower. If this transfer of pollen occurs in the same flower, it is referred to as self-pollination, whereas if the pollen is transferred from one flower to another, it is known as cross-pollination. This transfer is carried out by different agencies like wind, water, insects or animals.
Fertilization: A tube grows out of pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the female germ-cells present in ovule in the ovary. Out of two male gametes present in pollen tube one fuses with egg to form zygote. This fusion is called fertilization. After fertilization, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a tough coat and gradually turns into a seed. The ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form a fruit. Meanwhile the petals, sepals, stamens, style and stigma may shrivel and fall off.
15. Reproduction in human beings : The reproductive organs of human beings are called gonads. These are testes in male and ovaries in female. The male gonad produces sperms and female gonad produces ova (eggs) at the age of puberty (after attainment of sexual maturity). Various changes occur in girls and boys at this age.
16. Male Reproductive System consists of the following organs:
Testes: A pair of testes are situated in scrotum that lie outside the abdominal cavity and behind the penis. Testes produce sperms and hormone, Testosterone hormone. Testosterone brings about changes in appearance of boys at the time of puberty.

VAS deferens: From each testis, a duct arises which is known as vas deferens which unites with a tube coming from urinary bladder. It brings sperms from testis.
Urethra: Vas deferens tube opens into a common tube called urethra. It runs through a muscular organ called Penis. Penis is male copulatory organ.
Accessory Glands: Glands like prostate and seminal vesicles and Cowper’s gland add their secretions which make transport of sperms easier and this fluid also provides nutrition.
17. Female Reproductive System: It consists of the following organs:

Ovaries: Paired ovaries are located in the abdominal cavity near the kidney. Ovaries produce female gamete (ovum or egg) and secrete female hormones (estrogen and progesterone). One egg is produced every month alternately by one of the ovaries.
Fallopian Tube: The egg is carried from the ovary to womb/uterus through a thin oviduct or fallopian tube.
Uterus: The two oviducts unite into an elastic bag like structure known as the uterus.
Vagina: Uterus opens into the vagina. It is a female copulatory organ.
18. Sexual Cycle in female: After puberty, only one egg is produced alternately from one ovary after a period of 28 days. Egg in fallopian tube encounter sperms which enter through the vaginal passage during sexual intercourse. This fertilized egg (zygote) gets implanted in the lining of uterus which later forms embryo. Embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of special tissue called placenta.
If the egg is not fertilized, if lives for about one day since the ovary releases one egg every month, the uterus prepares itself every month to receive the fertilized egg. Thus, its lining becomes thick and spongy. If it does not get zygote, the developed lining slowly breaks down and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucus. This cycle takes place roughly every month and is known as menstruation. It usually lasts for about 2-5 days.
19. Reproductive Flealth: Reproductive organs need a lot of care and hygiene. Otherwise, they are susceptible to many infections or diseases. The diseases which spread through sexual routes are known as sexually transmitted diseases e.g., bacterial infections like syphilis, gonorrhoea and viral infections such as warts and HIV- AIDS. A condom helps to prevent transmission of many of these infections to some extent.
Frequent pregnancy causes many health problems and also adds to an already exploding population. Many ways have been devised to avoid pregnancy. Contraception can be achieved by:
- Mechanical barrier method (use of condoms).
- Chemical methods (use of pills).
- Use of contraceptive devices (copper-T).
- Surgical methods (vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females)
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
In a bisexual flower, inspite of the young stamens being removed artificially, the flower produces fruit. Provide a suitable explanation for the above situation.
Answer:
The open flowers are generally cross pollinated. Removal of stamens of a bisexual flower will not affect pollination of its intact pistil and formation of fruit.
Question 2.
Can you consider cell division as a type of reproduction in unicellular organisms ? Give one reason.
Answer:
Yes. Cell division in a unicellular organism which produces two d&ughter cells, actually forms two daughter individuals.
Question 3.
What is a clone ? Why do offspring formed by asexual reproduction exhibit remarkable similarity ?
Answer:
Clone is an exact genetic replica of another individual. All the offspring formed from a parent through asexual reproduction are clones of one another as well as their parent. The remarkable similarity of asexually produced daughter individuals is due to genetic similarity as they possess exact copies of DNA of their parent.
Question 4.
Explain how, offspring and parents of organisms reproducing sexually have the same number of chromosomes/DNAs.
(CCE 2014, CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
The parents are diploid (2n) as each of them has two sets of chromosomes (DNAs). They form haploid (In) male and female gametes through the process of meiosis. The haploid gametes have one set of chromosomes (DNAs). During fertilization, one male gamete fuses with one female gamete. It restores the diploid (2n) chromosome/DNA number in the offspring that is formed from fusion product or zygote (2n).
Question 5.
Colonies of yeast fail to multiply in water but multiply in sugar solution. Give one reason for this.
Answer:
Yeast is heterotrophic. It obtains its nourishment from outside. Plain water cannot provide nourishment to yeast while sugar solution can do so. Therefore, Yeast multiplies in sugar solution and not in plain water.
Question 6.
Why does Bread Mould grow profusely on a moist slice of bread rather than on a dry slice of bread ?
Answer:
Growth of Bread Mould requires both water and nutrients. Dry slice of bread contains nutrients but no water. Therefore, Bread Mould does not grow over it. Moist slice possesses both water and nutrients. Hence, Bread Mould grows over it.
Question 7.
Give two reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction.
Answer:
Variations appear in the progeny of sexually reproducing organisms due to
- Random separation and coming together of chromosomes during gamete formation and gamete fusion
- Crossing over and mutations.
- Coming together of chromosomes of the parents.
Question 8.
Would a Planaria cut vertically into two halves regenerate into two individuals ?
Answer:
Yes. Each piece of Planaria is able to grow the missing parts and form the complete organism.
Question 9.
Correlate the number of chromosomes with the size of the organism and answer the following questions :
(a) Do larger organisms have more number of chromosomes/cell ?
(b) Can organism with fewer chromosomes reproduce more easily than organism with more number of chromosomes ?
(c) More the number of chromosomes/cell, greater is the DNA content. Justify.
Answer:
(a) No. There is no correlation between chromosome number and size of the individual.
(b) No. Chromosome number does not affect reproduction.
(c) Yes. Each chromosome represents a single duplex of DNA. More chromosomes means more DNA.
Question 10.
In Tobacco, male gametes have 24 chromosomes.
(a) What is the number of chromosomes in the female gamete ?
(b) What is the number of chromosomes in the zygote ?
Answer:
(a) 24
(b) 48.
Question 11.
Why cannot fertilization take place in flowers if pollination does not occur ?
Answer:
Pollination is essential for bringing the male gametes. In the absence of pollination, there will be no male gamete to perform fertilization.
Question 12.
Is the chromosome number of zygote, emboryonal cells and adult of a particular organism always constant ? How is the constancy maintained in these three stages ?
Answer:
Zygote is the first diploid structure. It undergoes mitotic divisions to form embryonal cells. Embryonal cells further divide by mitosis to form the adult. Mitosis maintains the same chromosome number in the daughter cells.
Question 13.
Where is the zygote located in the flower after fertilization ?
Answer:
Zygote is the fertilized oosphere which occurs in the embryo sac present inside an ovule located in the ovary part of the pistil.
Question 14.
Reproduction is linked to stability of population of a species. Justify the statement.
Answer:
Reproduction maintains the size and composition of population of a species by regularly adding new individuals for replacing the ones getting killed due to ageing, disease or predation. It also adds variations that allow the individuals to adapt to changing environment.
Question 15.
How are general growth and sexual maturation different from each other ?
Answer:
General growth is the growth of an individual in size, height, shape, weight, etc. Sexual maturation is a set of changes in body of an individual that enable one to take part in reproduction, e.g., maturation of gonads, genitalia and other accessory structures. In human beings, beginning of sexual maturation is indicated by puberty changes like cracking of voice, new hair pattern, development of breast in female, etc.
Question 16.
Trace the path of sperm during ejaculation and mention the glands and their function associated with the male reproductive system.
Answer:
Ejaculated sperms are the ones which are stored in epididymes. They are formed regularly in seminiferous tubules from where they pass through vasa efferentia into epididymes. At the time of ejaculation, the sperms are first pushed through vasa deferentia, enter ejaculatory duct where they receive secretion of seminal vesicles and then urinogenital duct where the secretion of prostate gland is poured to form semen. The urinogenital duct is lubricated by secretion of a pair of Cowper’s glands (bulbourethral glands).
Secretion of Seminal Vesicles. Nourishment, activation and providing fluid medium for sperm transport.
Secretion of Prostates Gland. Motility of Sperms.
Question 17.
What changes are observed in the uterus if fertilization does not occur ? (CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Glands present in the mucosa of uterine endometrium begin to degenerate. This sloughs off the endometrial lining, releasing a lot of mucus and blood. It is called menstruation. Menstruation lasts for 3-5 days.
Question 18.
What changes are observed in the uterus subsequent to implantation of young embryo ? (CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Endometrium thickens, becomes glandular and highly vascular. The contact region between embryo and uterine wall grows into placenta. Placenta helps the embryo in obtaining nourishment and oxygen from blood sinuses of the uterus. It also helps in transfer of wastes from embryo to the blood of the mother.
Question 19.
What are the benefits of using mechanical barriers during sexual act ?
Answer:
- Prevention of Pregnancy : Mechanical barriers (e.g., Condoms, diaphragms) prevent the passage of sperms into the genital tract of the female. Consequently, pregnancy does not occur.
- Non-transmission of Infections: There is no transfer of venereal diseases from the infected partner to the non-infected partner.
Question 20.
In the female reproductive system, name the parts that are involved in
(a) Production of egg.
(b) Site of fertilization
(c) Site of implantation
(d) Entry of sperms.
Answer:
(a) Production of Egg: Ovary
(b) Site of Fertilization: Ampulla part of fallopian tube.
(c) Site of Implantation: Uterus.
(d) Entry of Sperms: Vagina.
Question 21.
What would be the ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote ? How is the sperm genetically different from the egg ?
Answer:
Chromosome Number in Egg and Zygote. 1 : 2
Genetic Difference between Sperm and Egg. Sperms are genetically of two types, X-containing and Y-containing. Eggs are always of one type, X-containing.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Long Answer Questions
Question 22.
Why are budding, fragmentation and regeneration all considered as asexual types of reproduction ? With neat diagrams, explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
Answer:
(a) Asexual Reproduction: Budding, fragmentation and regeneration are all considered to be modes of asexual reproduction as they involve formation of new individuals from single parents without fertilization or fusion of gametes.
(b) Regeneration in Planaria:
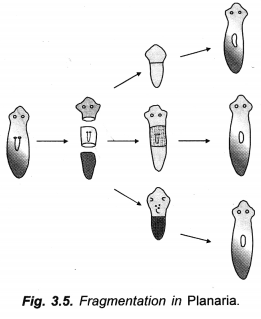
Question 23.
Write two points of differences between asexual and sexual types of reproduction. Describe why variations are observed in the offspring formed by sexual reproduction.
Answer:
(a) Differences between Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
| Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
| 1. Parents: It is monoparental. | It is generally biparental |
| 2. Meiosis: Meiosis does not occur during asexual reproduction. There are no gametes and no fertilization. | Meiosis occurs. Gametes are formed and fertilization occurs in sexual reproduction. |
| Ex. Binary fission in Amoeba, Budding in Yeast | Ex. Offspring in Wheat, Human. |
(b) Development of Variation in Sexual Reproduction:
Sexual reproduction produces a number of variations in the population due to
- Chance separation of chromosomes at the time of meiosis.
- Crossing over during meiosis.
- Chance combination of chromosomes during fertilization. It produces a unique combination of variations already accumulated by each individual in its DNA obtained from its parents,
- Mutations or defective DNA replication.
Question 24.
Distinguish between pollination and fertilization. Mention the site and product of fertilization in a flower. Draw a neat, labelled diagram of a pistil showing pollen tube growth and its entry into the ovule.
Answer:
(a) Differences between Pollination and Fertilization
| Pollination | Fertilization |
| 1. Definition: It is transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of a flower.
2. Step: Pollination precedes fertilization. 3. Purpose: It carries the male gamete producing pollen grains to the female sex organ. 4. Process: Pollination is a physical process. 5. Occurrence: It occurs only in seed plants. |
It is the fusion of male and female gametes.
Fertilization occurs only after pollination when the pollen grain has germinated and male gametes are carried into ovule. It actually brings about fusion of gametes. Fertilization is a physico-chemical (biological) process. It occurs in both plants and animals of various types. |
(b)
- Site of Fertilization. Embryo sac in ovule.
- Product of Fertilization. Zygote, Primary endosperm cell.
(c)
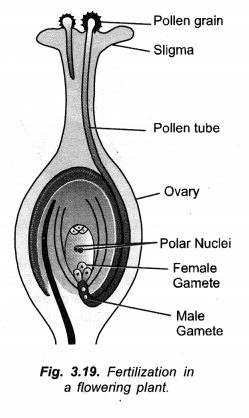
Question 25.
Distinguish between a gamete and zygote. Explain their roles in sexual reproduction.
Answer:
Differences between Gamete and Zygote
| Gamete | Zygote |
| 1. Nature: It is sex or germ cell that takes part in fertilization. | It is a product of fertilization. |
| 2. Types: There are two types of gametes, male and female. | Zygote is of one type. |
| 3. Chromosome Number: A gamete has haploid or In chromosome number. | Zygote has diploid or 2n chromosome number. |
| 4. Characteristics: A gamete carries characteristics of only one parent. | It carries characteristics of both the parents. |
| 5. Generation: Gamete is the last cell of its generation. | It is the first cell of new generation. |
Role of Gamete. Gamete is sex or germ cell which is specialized to take part in sexual reproduction. There are two types of gametes, male and female. Each of them carries one set of chromosomes which are randomly obtained from its parent. Fusion of male gamete with a female gamete produces a zygote.
Role of Zygote. It is the first’cell of new generation. Zygote develops into embryo that later forms the new individual.
Question 26.
Draw the diagram of a flower and label the four whorls. Write the names of gamete producing organs in the flower.
Answer:
(a)
(b) Male Gamete Forming Part. Pollen grain, produced in anther of stamen.
Female Gamete Forming Part. Embryo sac developed inside ovule of ovary part of pistil.
Question 27.
What is placenta ? Mention its role during pregnancy. (CCE 2011, 2014)
Answer:
Placenta: It is a special double layered, spongy tissue connection between the foetus and uternine wall found in pregnant females. It has finger-like outgrowths or villi which are in contact with blood sinuses present in the uterine wall.
Role:
- Attachment: Placenta attaches the foetus to uterine wall.
- Villi: Placenta has finger-like outgrowths or villi which develop a large surface area for fixation and absorption.
- Nutrients: Placenta picks up nutrients from mother’s blood and passes it to the blood of the foetus.
- Waste Products: Waste products produced by the foetus passes out through the placenta into mother’s blood.
- Gases: Foetus obtains oxygen supply from mother’s blood and eliminates carbon dioxide through placenta.
Question 28.
What are the various ways to avoid pregnancy ? Elaborate any one method.
Answer:
(a) Methods to Avoid Pregnancy: Prevention of pregnancy is called contraception. The techniques used in preventing the occurrence of pregnancy are called contraceptive devices.
(b) Mechanical Barrier Methods of Contraception:
- Mechanical Barriers like condoms, cervical cap, diaphragm.
- Oral Contraceptives or oral pills like Mala D, Saheli
- Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices (IUCD) like loop, bow, Cu-T.
- Surgical Methods like vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females.
Question 29.
Flow does fertilization take place ? Fertilization occurs once in a month. Comment.
Answer:
In human beings, fertilization is internal. It can occur within 2-3 days of ovulation (between 14th and 16th day of menstrual cycle). Fertilization generally takes place in ampulla (ampulla-isthmus border) part of fallopian tube where ovum rests for several hours after entry into oviduct. The sperms have to reach there. Sperms deposited in the vagina reach there partly by their own movement and partly by local movements of reproductive tract. Both sperms and eggs are viable for 24-48 hours. A sperm reaching the surface of ovum, dissolves its covering and passes its head and middle part into it. It results in fertilization and formation of zygote.
Fertilization only once in a Month. A single ovum is released by female roughly in the middle of menstrual cycle which has a span of 4 weeks. Therefore, fertilization can occur only once in a month.
Question 30.
Reproduction is essentially a phenomenon that is not for survival of individual but for the stability of a species. Justify. Reproduction is not essential for survival of the individual.
Answer:
Survival of the individual depends upon input of nutrients and energy and elimination of wastes. Reproduction has ho role in these. It is, however, essential for the stability and survival of the species. Reproduction takes part in
(a) Perpetuation of Species: Perpetuation or continuation of species.
(b) Replacement: Replacement of dead individuals and maintaining the organisation in population.
(c) Population Characteristics:
- Education: There is an inverse ratio between education and population growth.
- Population Education: It is imparting knowledge to public about the effects of excessive population, advantages of small families and means to achieve it.
- Marriageable Age: Number of births is reduced if young persons marry late. Gainful employment and higher social status of women also reduce birth rate.
(d) Variations:
Variations are differences found in morphological, physiological and other traits of individuals belonging to the same organism, race or family. They develop due to
- Faulty DNA replication
- Crossing over
- Chance separation of chromosomes during meiosis and chance combination during fertilization. Variations are highly important.
(e) Absence of Variations: Due to absence of variations, asexually reproduced organisms are unable to adapt themselves to changes in the environment.
Question 31.
Describe sexually transmitted diseases and mention the ways to prevent them.
Answer:
It is a group of infections caused by different types of pathogens that are transmitted by sexual contact between a healthy person and an infected person. The sexually transmitted diseases are also called venereal diseases (VDs). Some 30 different types of STDs are known.
- It is caused by bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Gonorrhoea spreads through sexual contact, common toilets and under clothes. Incubation period is 2-5 days. Bacterium resides in genital tubes. It causes pus containing discharge, pain around genitalia and burning sensation during urination. Effective medicine is ampicillin.
- The disease is caused by corkscrew like bacterium Treponema pallidum. It spreads through sexual contact and from mother to infants. Incubation periods is 3-5 weeks, Painless ulcer on genitalia and swelling of lymph glands occur in first stage. In second stage skin lesions, rashes and hair loss occur. Tertiary stage is characterised by chronic ulcers and damage to vital organs. Effective medicine is tetracycline.
- Genital Warts: The disease is due to Human Papilloma virus (HPV). Hard benign outgrowths called warts appear over external genitalia and perianal area. In women infection may enter vagina and cervix causing acute pain. Cryosurgery and Podophyllum preparations are effective.
- AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome): It is caused by human immunodeficiency virus or HIV. The virus is transmitted through sexual contact, blood contact (as using common needles, syringes, razors, transfusion) and placenta (mother to foetus). Incubation period is generally 27-28 months but symptoms may appear early. Count of T-helper cells becomes low, 200/ml or less. There is headache, rashes, nausea, pharyngitis and fever. Immunity is drastically reduced so that many infections (opportunistic infections) begin to appear. A proper treatment has not yet been discovered. ART (antiretrovirus treatment) is given to patients to reduce the effect of infection.
Extra Questions – How do Organisms Reproduce – CBSE Class 10 Science
Question-1
Name the various types of asexual reproduction.
Solution:
The various types of asexual reproduction are
• Fission – binary and multiple
• Budding
• Spore formation
• Regeneration
• Vegetative propagation – It is a process by which new organisms arise without production of seeds or spores. It can occur naturally or be induced by horticulturists.
Question-2
Differentiate between binary fission and multiple fission.
Solution:
Binary Fission:
1.In this type of fission, the parent cell gives rise to two daughter cells.
2.It is expressed by organisms like amoeba, paramecium, etc.
Multiple Fission:
1.In this type of fission , the parent cell gives rise to more than two daughter cells.
2.It is expressed by organisms plasmodium.
Question-3
List the advantages of vegetative propagation.
Solution:
The advantages of vegetative propagation are as follows
• It helps in the easy propagation of non–flowering plants.
• It helps in producing hybrids of various plants, with improved qualities.
• It helps in the propagation of a large number of populations in a very short duration.
• It helps in the propagation of plants that do not produce seeds or produce them in very small quantities.
Question-4
Name the male and the female gametes in human beings.
Solution:
The male gamete is called sperm and the female gamete is called ovum in human beings.
Question-5
Define fertilization.
Solution:
The process of fusion of the male gamete with the female gamete of the same species, i.e., the sperm with the ovum is known as fertilization. After fertilization, the product obtained is the zygote, which eventually develops into a complete organism.
Question-6
Define sexual reproduction.
Solution:
The type of reproduction that involves both the sexes of the species is known as sexual reproduction. This kind of reproduction requires the fertilization of the gametes of both the sexes.
Question-7
Mention any two functions of human ovary.
Solution:
The two functions of human ovary are as follows
(i) It is responsible for the production of the female gamete, ovum.
(ii) It secretes hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
Question-8
What is syngamy?
Solution:
The process of fusion of the two gametes is known as syngamy. It is the initial step in the process of fertilization.
Question-9
Where does fertilization take place in human females?
Solution:
Fertilization in the case of humans is internal. The process of fertilization takes place inside the fallopian tube of females.
Question-10
Define menopause.
Solution:
At the age of around 45-50 years, the ovaries of the females stop producing ova.
The stoppage of menstrual flow and other events like the changes in the hormonal composition is known as menopause.
Question-11
Discuss briefly the types of reproduction.
Solution:
Reproduction is a unique biological process that is essential for the continuity and propagation of species. It is a process by which new individuals of the same species are produced by parental organisms. It takes place by two methods: –
Asexual Reproduction
This method of reproduction generally involves only one parent and is observed only in lower organisms. Fission, budding, spore formation and vegetative propagation are some of the types of asexual propagation.
Sexual Reproduction
This method of reproduction involves two parents. It requires the fusion of gametes of both the sexes of the species. Almost all animals and higher forms of plants reproduce by this method.
Question-12
Describe asexual reproduction in amoeba.
Solution:
Amoeba reproduces by the process of binary fission. During this process, the nucleus divides first, followed by the formation of a constriction in the cellular membrane of amoeba. This gradually increases inwards and divides the cytoplasm into two parts. Finally two daughter organisms are obtained.
Question-13
Explain various steps of budding in yeast.
Solution:
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction usually observed in yeast.
• During this process, a small protrusion appears on the upper portion of the body of the organism. This bulge is called a bud.
• The bud gradually grows in size and forms an individual cell.
• From this newly budded cell, another bud appears at the tip.
• This process continues and a chain of yeast cells is obtained.
Question-14
What are the various methods of vegetative propagation? Discuss any one method with example.
Solution:
The various types of vegetative propagation are
• Cutting
• Layering
• Grafting
• Parthenogenesis
• Micro-propagation in vitro
Grafting
• It is a method in which two parts of different plants are joined together in such a way that they unite and grow as one plant.
• The portion of the plant that is grafted onto another plant is known as the scion, and the plant on which grafting is performed is known as the stock.
• The stock and the scion are tied in such a way that the cambium of the scion and the stock come in contact with each other.
• The stock is so chosen that it possesses qualities like disease resistance, high water absorbing capacity, deep penetrating roots for a firm hold, etc. The scion is so chosen that it possesses qualities like high yield of pulp or seeds (as desired) from a single fruit, etc.
• For example citrus-root stock is used for a variety of grafts like sweet orange, lime, grape, etc.
Question-15
Define the terms unisexual and bisexual giving examples of each.
Solution:
An animal or an organism, which can be differentiated as male or female.
i.e., The two sexes are present in separate individuals, then such an organism is said to be unisexual.For example, human beings, all mammals. An animal or an organism that possesses both the sexes in a single body is said to be a bisexual animal. For example, earthworm, starfish, etc.
Question-16
Mention the reproductive parts of a flower.
Solution:
The reproductive parts of a flower are as follows
Male reproductive part – Stamens
Female reproductive part – Pistil.
Question-17
What is pollination? Describe cross-pollination.
Solution:
The transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma is called pollination. Pollen grains are shed from the anther and reach the stigma of either the same flower or a different flower.
Cross-pollination
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same species is termed as cross-pollination.
Question-18
Describe double fertilization in plants.
Solution:
In the case of plants, the pollen grain releases two male gametes. One fuses with the egg and forms the zygote. The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei. This fusion is said to be triple fusion. Thus, inside an embryo sac, two fusions, syngamy and triple fusion, take place. This mechanism of two fusions occurring in an embryo sac is called double fertilization.
Question-19
What are the male and the female gonads in the human beings? Mention their functions.
Solution:
Testes are the male gonads in human beings. Their functions are
• To produce male hormones like testosterone.
• To produce the male gamete – sperm.
Ovaries are the female gonads in human beings. Their functions are
• To produce female hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
• To produce the female gamete – ovum.
Question-20
Mention the secondary sexual characters in human males and females.
Solution:
The male secondary sexual characters are the growth of hair on the chest, near the genitals, on the face in the form of beard and moustache, development of deep hoarse voice, etc.
The female secondary sexual characters are the development of breasts and mammary glands, axial and pubic hair, etc.
Question-21
Write names of one male and female sex hormones.
Solution:
The names of one male and one female sex hormones are as follows
Male sex hormone – testosterone
Female sex hormone – progesterone.
Question-22
Describe the menstrual cycle.
Solution:
• The commencement of menstruation at puberty is termed menarche and marks the beginning of the reproductive life of a female.
• Initially, inside the ovary, an oogonium or an ovarian follicle is developed into a mature ovum and released into the fallopian tube. This is termed as ovulation.
• After the release, the uterus and the fallopian tubes undergo changes like the thickening of the uterine wall, development of the endometrial lining, etc. to prepare the body for a probable pregnancy.
• If fertilization does not occur, then the thickened inner wall of the uterus breaks down along with its blood vessels and moves out of the vagina in the form of bleeding, called menstrual flow (menstruation).
• It lasts for about 4-7 days.
• This cycle of events taking place in the ovaries and the uterus every 28 days and marked by the menstrual flow is known as the menstrual cycle.
• In a normal healthy woman, ovulation takes place around the 14th day and menstruation occurs every 28 to 30 days.
Question-23
Differentiate between menarche and menopause.
Solution:
• Menarche marks the beginning of the reproductive cycle of a female whereas menopause marks the end of the reproductive cycle.
• Menarche generally takes place at puberty, i.e., at the age of 12-16 years while menopause takes place around the age of 45-50 years.
• After menarche, there is an increased amount of production of female sex hormones whereas after menopause, the secretion of female sex hormones declines and sometimes completely stops.
Question-24
What is ovulation?
Solution:
The ovarian follicles present inside the ovaries develop into mature follicles. Usually, one mature ovarian follicle develops into a mature ovum. It pinches off from the surface of the ovary and enters the fallopian tube. This process is termed as ovulation. Generally ovulation takes place in only one ovary at a time.
Question-25
Write whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Fertilization is the fusion of the sperm and the ovum.
2. Duration of menstrual cycle in human female is 20 days.
3. Onset of menstruation is termed menopause.
4. In human beings, male attains puberty little later than females.
Solution:
1. True
2. False
3. False
4. True.
Question-26
Fertilization is possible if copulation has taken place during the middle of the menstrual cycle.Give reasons.
Solution:
During copulation, a large number of sperms enter the fallopian tube. If copulation takes place during the middle of the menstrual cycle, then fertilization is possible as at this time the ovum would have entered the fallopian tube from the ovary. If copulation takes place before ovulation then fertilization is not possible. Fertilization is marked by the absence of the regular menstrual flow.
Question-27
Mention the methods used for regulation of childbirth.
Solution:
A number of techniques are employed for the regulation of childbirth. They are classified as follows
Barrier methods – Use of physical devices to prevent the entry of sperms inside the female genitals. They include:
1. Condoms
2. Diaphragms
3. Cervical caps
4. Intrauterine contraceptive devices (IUCD) like Copper-T.
Chemical methods – Use of specific drugs by females.
1. Oral pills – Oral contraceptives of mainly hormonal preparations.
2. Vaginal pills
Surgical methods –
1. Vasectomy – Removal or ligation of a small portion of the vas deferens in males.
2. Tubectomy – Removal or ligation of a small portion of fallopian tube in females.
Question-28
Write the full forms of IUCD, AIDS, HIV, and OC.
Solution:
The full forms for the above abbreviations are as follows
IUCD – Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices
AIDS – Acquired Immuno-Deficiency Syndrome
HIV – Human Immuno Virus
OC – Oral Contraceptives.
Question-29
Describe the surgical method of birth control.
Solution:
In the surgical methods of birth control, a small portion of vas deferens in males and the fallopian tube in females is surgically removed or ligated (tied). This process is called Vasectomy in males and Tubectomy in females. As a result of this surgery, gametes cannot be released from the body (in males) and cannot enter the uterus (in females).
Question-30
Define sexually transmitted disease and give two examples.
Solution:
There are certain infectious diseases that spread by sexual contact. Such diseases are called STDs (Sexually Transmitted Diseases). In most cases, the symptoms are burning sensation on urination and urethral discharge. Gonorrhea and Syphilis are the two examples for sexually transmitted diseases. These diseases are curable.
